Figure 8.
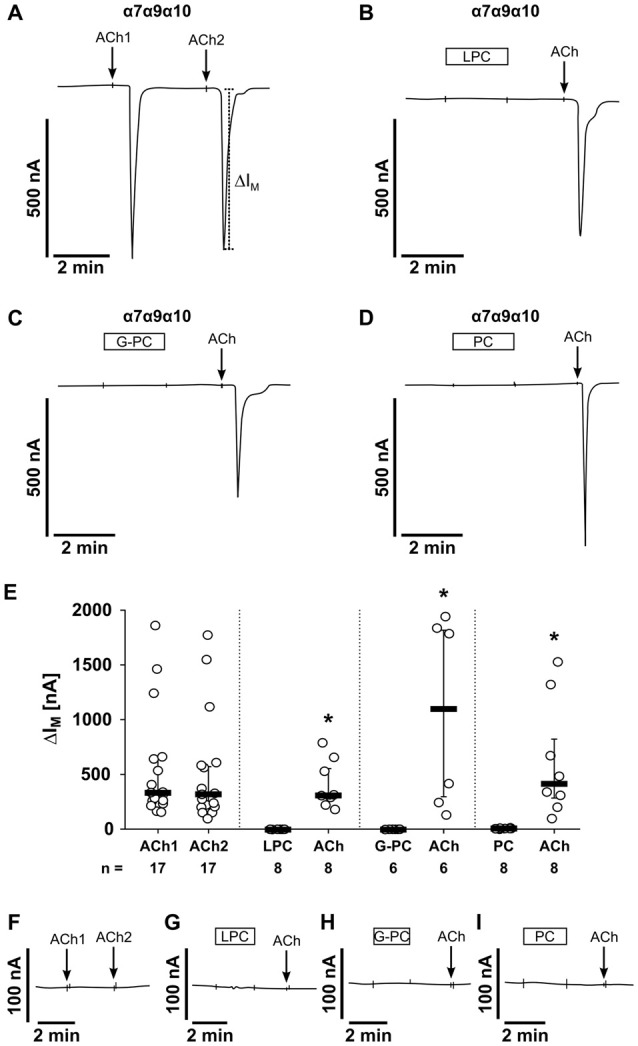
LPC, G-PC and PC do not induce ion channel functions at oocytes co-expressing nAChR subunits α7, α9 and α10. Two-electrode voltage-clamp (TEVC) measurements were performed on Xenopus laevis oocytes that heterologously co-expressed human α7, α9 and α10 nAChR subunits. (A) Representative current curve. The application of ACh (100 μM; 1 s) induced repetitive responses of transmembrane ion currents (∆IM; ACh1 and ACh2). (B–D) Initial application of LPC (100 μM; 2 min) (B), G-PC (100 μM; 2 min) (C) as well as PC (100 μM; 2 min) (D) had no impact on ∆IM, whereas ACh induced a current response. (E) Graphical representation of the results of experiments as shown in (A–D). (F–I) In water-injected control oocytes neither repeated application of ACh (n = 16), nor application of LPC (n = 6), G-PC (n = 4) or PC (n = 6) had any effect on ∆IM. All changes of ∆IM induced by cholinergic stimulation are shown as individual data points, bars represent median, whiskers percentiles 25 and 75. Statistical analyses were performed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. *p ≤ 0.05 significantly different from the ∆IM values before.
