Fig. 3. The Lin-CD34+CD38+ compartment consists of distinct lineage-restricted progenitors.
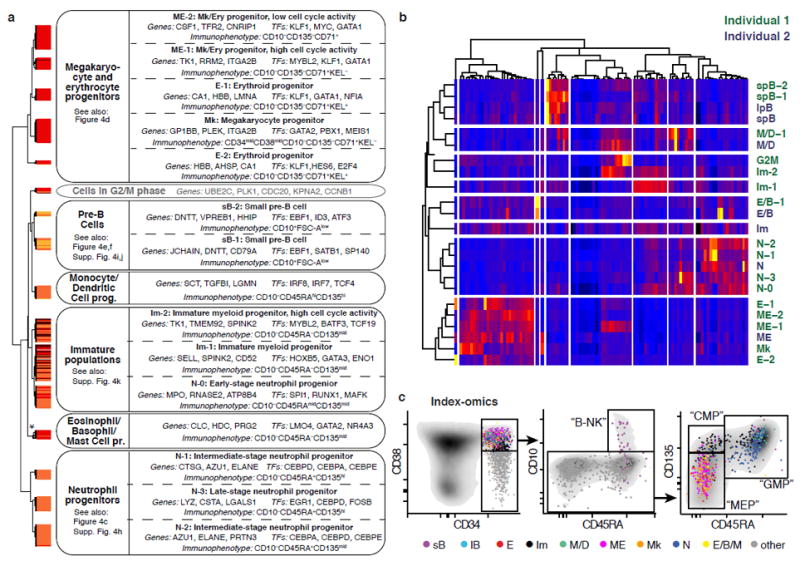
(a) Overview of putative cell types in individual 1 (see panel b for a comparison between individuals). Classes obtained from hierarchical clustering of the Lin-CD34+CD38+ compartment (Fig. 2a) were assigned to putative cell types based on analyses of gene- and surface marker expression. The asterisk indicates that 3 putative Eosinophil/Basophil/Mast cell progenitor subclusters of <5 cells were merged for this analyses. (b) Averaged gene expression profiles for cell types from both individuals defined in Fig. 2a were clustered based on the 1000 most variable genes. Only the most variable 100 genes are shown in the heatmap. (c) Index-omics display of Lin-CD34+CD38+ progenitors. Sequenced single Lin-CD34+CD38+ cells were arranged according to their cell surface marker expression in classical FACS gating strategies to identify B- and NK cell progenitors (“B-NK”), Megakaryocytic-Erythroid Progenitors (“MEP”), Common Myeloid Progenitors (“CMP”) and Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors (“GMP”). Cells were colour-coded based on their cell type identity from Fig. 3a.
