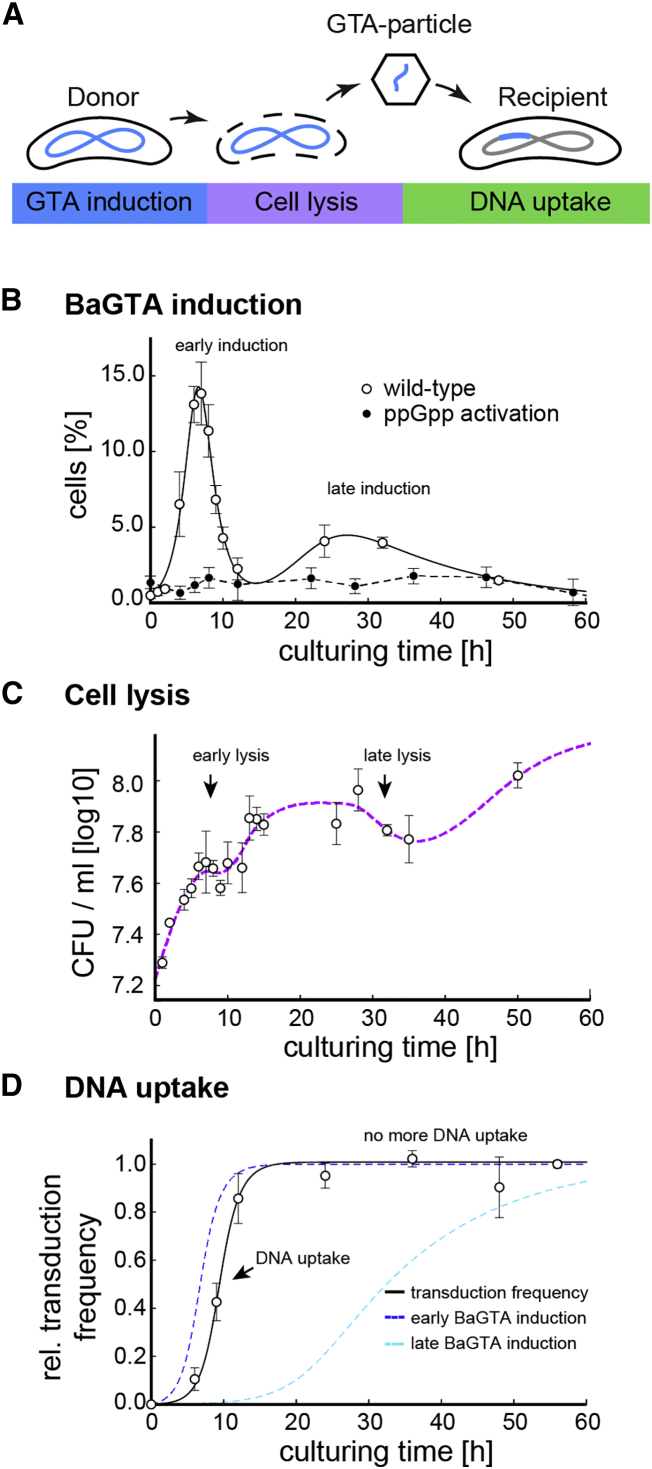
Figure 1.
Chromosomal Marker Exchanges during B. henselae Co-culture
(A) Schematic model for BaGTA-mediated genetic exchange in Bartonella. In a three-stage process, induction of BaGTA in donor cells (blue) leads to host cell lysis (purple) and release of BaGTA particles that are taken up by recipient cells (green).
(B) Induction dynamics of the BaGTA locus as detected by FACS analysis of gfp-bgtC reporter strain upon cultivation of Bartonella in M199. A subpopulation of wild-type cells synchronously induces BaGTA locus (open circles) leading to early and late peaks in GTA induction. BaGTA induction is absent in cells expressing the constitutive active ppGpp synthase gene RelA1–455 from E. coli, suggesting that elevated levels of ppGpp repress induction of BaGTA. The mean values from a biological triplicate and their associated SEs are displayed.
(C) Cell density upon cultivation in M199 is shown as a spline fit (dotted line, purple) to the experimental growth data as determined by CFU counts. A temporal decrease in viable cells around 10 and 30 hr indicates BaGTA-induced cell lysis (early and late lysis). The mean values and associated SD from a biological triplicate are displayed.
(D) Relative transduction dynamics as a function of the co-culturing time are shown. The experimentally determined DNA uptake rate (transduction frequency, open circles) follows a time-delayed function (black line) proportional to the integrated GFP-expression rate of the first BaGTA induction peak (blue dashed line), while the integrated GFP-expression rate of the second BaGTA induction peak (cyan dashed line) does not contribute to detectable DNA uptake. The mean values from a biological triplicate and their associated SEs are displayed.