Figure 4.
Identification of Bartonella Genes Involved in BaGTA Uptake
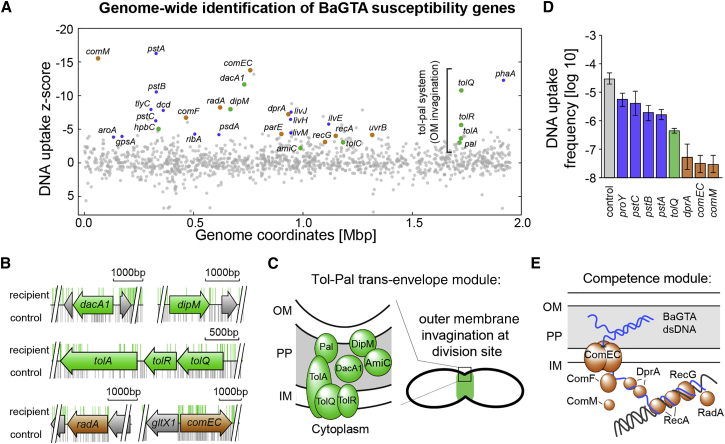
(A) DNA uptake Z-score calculated by comparative TnSeq analysis reveals genes involved in the uptake and incorporation of BaGTA DNA in recipient bacteria. Negative values indicate a decrease of BaGTA uptake and positive values, an increase. Highlighted are components of the Tol-Pal trans-envelope module (green) belonging to the divisome machinery and the identified competence and recombination pathway (brown). Metabolic components that presumably impair cell division such as the putative proline-specific permease proY or three components of the Pts (phosphate transport system) encoded by pstA, B, and C are highlighted in purple.
(B) Genome annotation track for selected genes with himar insertions recovered from control (gray bars) and recipient experiment (green bars).
(C) Scheme of the identified components of the Tol-Pal trans-envelope module involved in BaGTA particle uptake. OM, outer membrane; PP, periplasm; IM, inner membrane.
(D) Validation of the TnSeq results by co-cultivation experiments using individual Tn insertion mutants. Displayed are the averaged log10 transformed frequency of double resistant bacteria (log recipient frequency) obtained after 24 hr co-culture and associated SDs (n = 3). Mutations in the competence genes dprA, comEC, and comM and the outer circle components proY and pstA, B, C affecting cell-growth (blue) show reduced DNA uptake rates compared with the wild-type control. The control specifies a wild-type strain with an antibiotic marker at a neutral locus.
(E) Scheme of the identified competence module required for BaGTA DNA uptake. See also Figure S3.