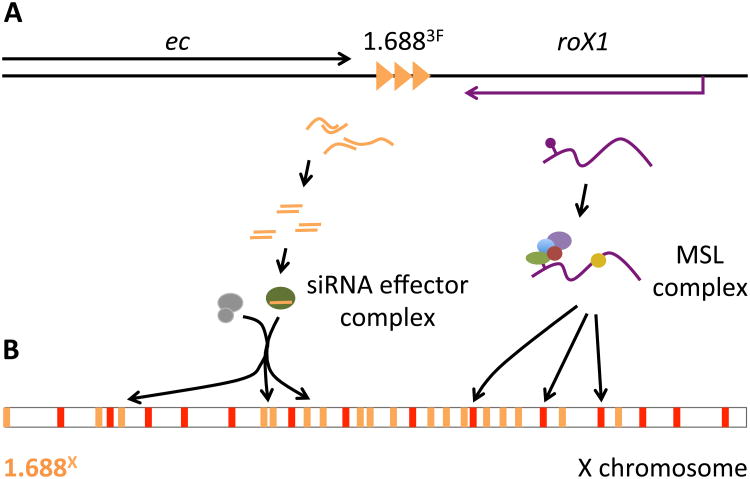
Fig. 6. Linkage of 1.6883F and roX1 could coordinate function.
A) 1.6883F is located between echinus (ec) and roX1. Bidirectional transcription of 1.6883F may generate siRNA that is loaded onto an effector complex (left). Ago2, and other genes in the siRNA pathway, participate in X recognition [20]. The roX1 transcript is assembled into the MSL complex (right). roX1 and 1.6883F produce different classes of noncoding RNA, and each element retains biological activity when separated from the other. It is possible that the proximity of 1.6883F and roX1 coordinates different pathways that cooperate to identify X chromatin. B) A siRNA-containing effector complex may recruit chromatin modifiers (gray) to 1.688X repeats (gold) across the euchromatic X chromosome. We hypothesize that this produces epigenetic or architectural changes that facilitate MSL recruitment, or spreading of the MSL complex along the X. The MSL complex is initially recruited to Chromatin Entry Sites (CES, red), and spreads into active genes nearby. No direct association between proteins of the siRNA pathway and the MSL complex has been reported, suggesting that the siRNA pathway influences MSL recruitment indirectly.