Figure 1.
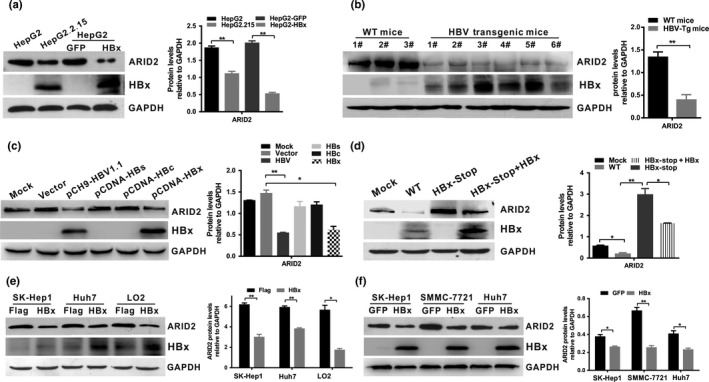
HBx downregulated ARID2 expression in hepatoma cells. (a) ARID2 and HBx protein was detected by western blot analysis in HepG2.2.15 cells and HepG2 cells infected with adenoviruses expressing HBx or GFP control (n = 3, **P < 0.01). (b) ARID2 and HBx protein expression in HBV‐transgenic mice and WT littermates (WT mice; **P < 0.01). (c) HepG2 cells were transfected with pCH‐9(HBV1.1), pCDNA‐HBs, pCDNA‐HBc, pCDNA‐HBx, or vector plasmid. ARID2 and HBx protein was detected using western blotting (n = 3, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (d) HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with full‐length HBV (WT‐HBV), stop‐mutant HBx (HBx‐stop), or stop‐mutant HBx plasmids plus adenovirus encoding HBx. ARID2 and HBx expression was determined by western blot analysis (n = 3, * P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (e,f) Western blot analysis of ARID2 and HBx expression in Sk‐Hep1/Sk‐Hep1‐HBx, Huh7/Huh7‐HBx, LO2/LO2‐HBx, and HBx‐transduced hepatoma cells. All data were acquired from three independent experiments, and representative results are shown. Integrated density was quantitatively analyzed using ImageJ software. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, Student's t‐test.
