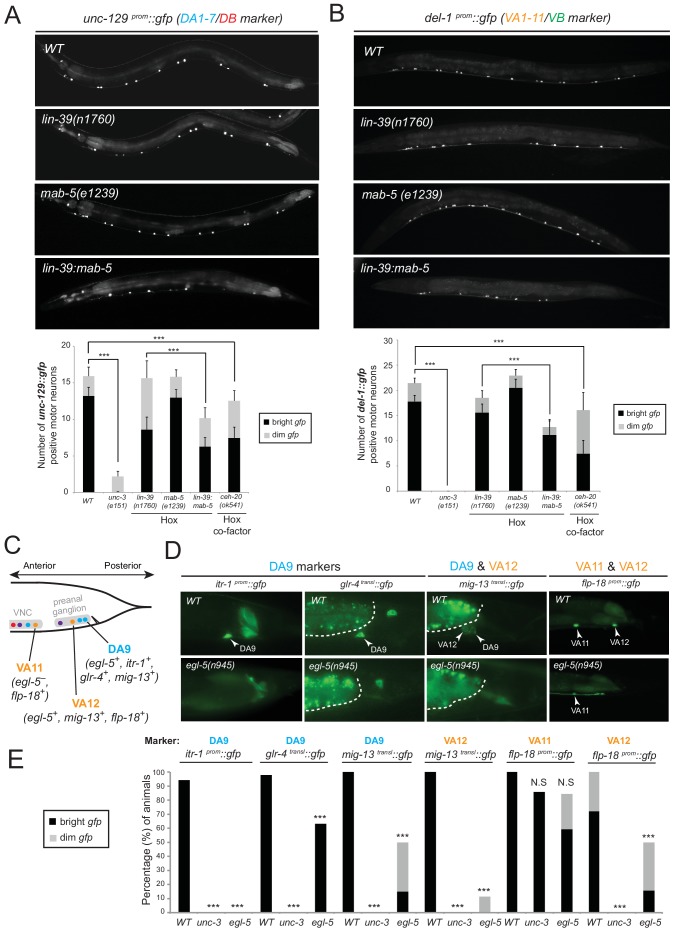
Figure 4. Hox genes – like unc-3 – control the expression of MN subclass-specific genes along the A-P axis.
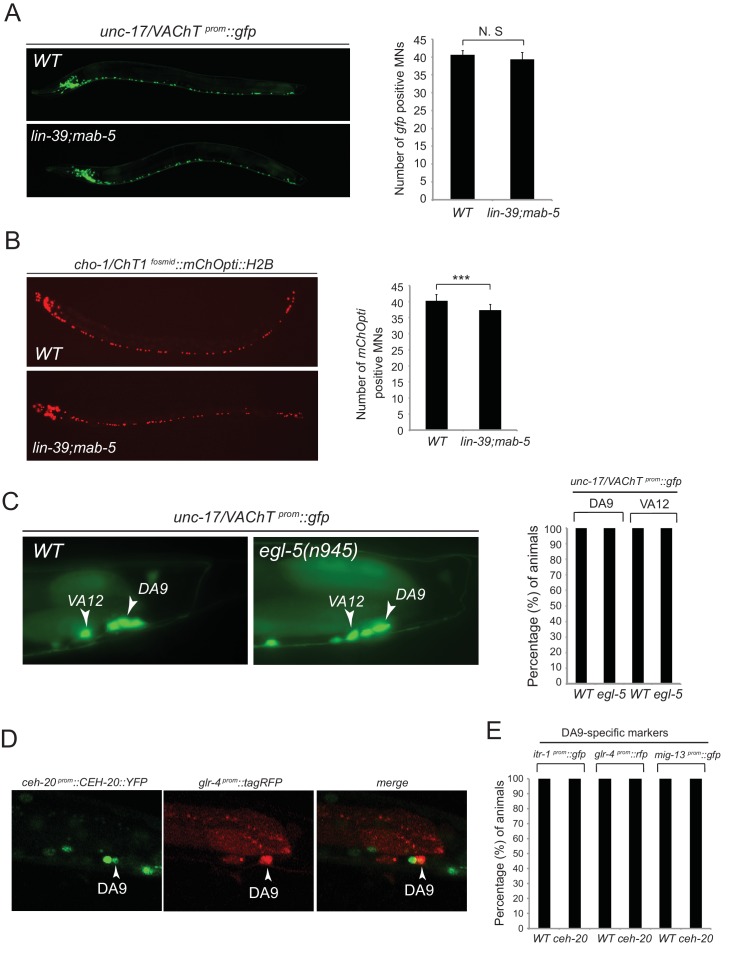
(A–B) The expression of the subclass-specific markers unc-129 (DA1-7/DB) and del-1 (VA1-11/VB) is significantly affected in lin-39 mab-5 double mutants, as well as in animals lacking ceh-20, C. elegans PBX homolog known to function as Hox co-factor. Quantification of the number of MNs expressing the gfp reporter (bright or dim) is provided at the bottom. Effects on reporter expression are milder in Hox null mutants when compared to unc-3 null mutants. Error bars represent standard deviation (STDV). ***p value < 0.001. N > 20 animals. (C–D) The posterior Hox gene egl-5/Abd-B/Hox9-Hox13 controls subclass-specific genes (itr-1, glr-4, mig-13, flp-18) expressed in the most posterior member of the DA (DA9) and VA class (VA12). Effects on reporter expression are milder in egl-5 null mutants when compared to unc-3 null mutants. Similar effects were observed for multiple egl-5 loss-of-function alleles (n945, u202, tm4746). A dotted white line marks the limit of the intestinal cells. (E) Quantification (percentage of animals) is provided with grey bars representing very dim gfp expression in the respective neuron, while black bars represent bright gfp expression. ***p value < 0.001. N > 20 animals.