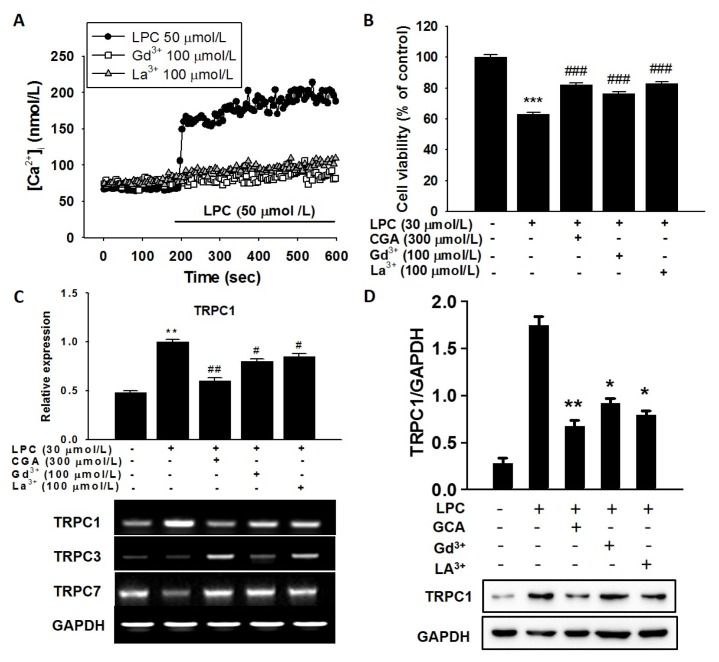
Fig. 3.
Effects of store-operated channel (SOC) blockers on lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC)-induced [Ca2+]i in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). (A) SOC blockers inhibited the LPC-induced sustained [Ca2+]i increase. (B) Comparative effects of chlorogenic acid (CGA) and SOC blockers on LPC-induced cell death in HUVECs. CGA increased cell survival to the same levels as the SOC blockers. (C) Inhibitory effects of CGA on LPC-induced expressions of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) channels 1, 3, and 7 in HUVECs. (D) Immunoblotting for the TRPC1 protein under treatment by CGA and SOC blockers in HUVECs. The bar graph shows that CGA significantly suppressed LPC-induced TRPC1 mRNA expression with similar potency to gadolinium (Gd3+) and lanthanum (La3+). PCR data normalized to GAPDH are expressed as the mean values of three separate experiments. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with a corresponding single treatment with the vehicle control; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared with a corresponding single treatment with 30 μmol/L LPC.