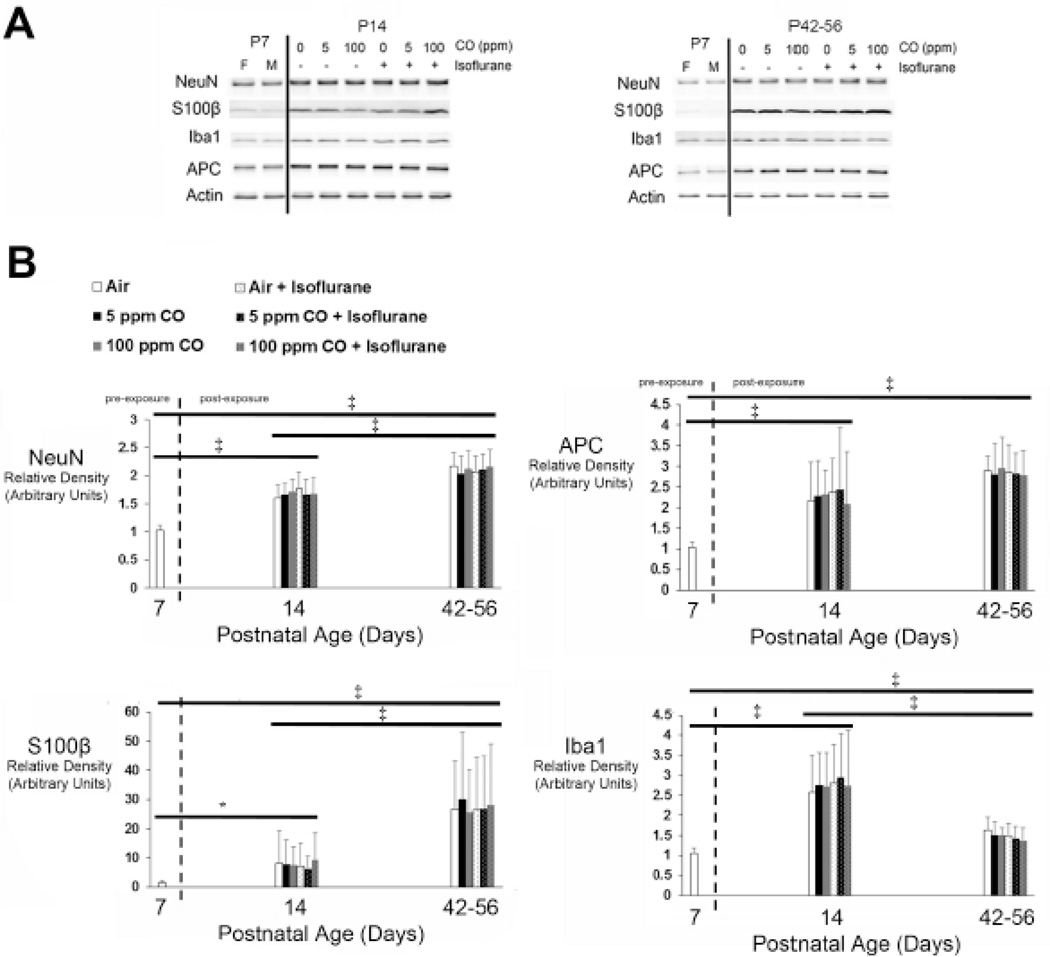
Figure 4. Cell-specific protein content in whole brain following exposure.
Steady-state levels of neuron-, astrocyte-, oligodendrocyte-, and microglial-specific protein were quantified in whole brain 1-week (postnatal day 14) or 5–7 weeks (postnatal days 42–56) post exposure. Seven-day old naïve female #3 and male #1 mice were arbitrarily chosen as representative unexposed controls to permit age-based comparison. A. Representative immunoblots of neuron specific antigen (NeuN), S100β, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), and ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1) are depicted for postnatal day 14 (P14) and postnatal days 42–56 (P42–56) time points. Actin was used as a loading control. Exposure cohorts are indicated by concentration of carbon monoxide (CO) (0 parts per million (ppm) [air], 5 ppm, or 100 ppm) with (+) or without (−) isoflurane. P7 female (F) and male (M) are indicated. B. Graphical representation of relative densities of NeuN, S100β, APC, and Iba1 are shown. Dotted line separates pre- and post-exposed cohorts. Values are expressed as means plus standard deviation. Unexposed, naïve P7 male values were arbitrarily set to 1. N = 10 animals for each exposed cohort per time point. *P < 0.05, ‡ P < 0.001. Significance post-exposure was within exposure cohort only.