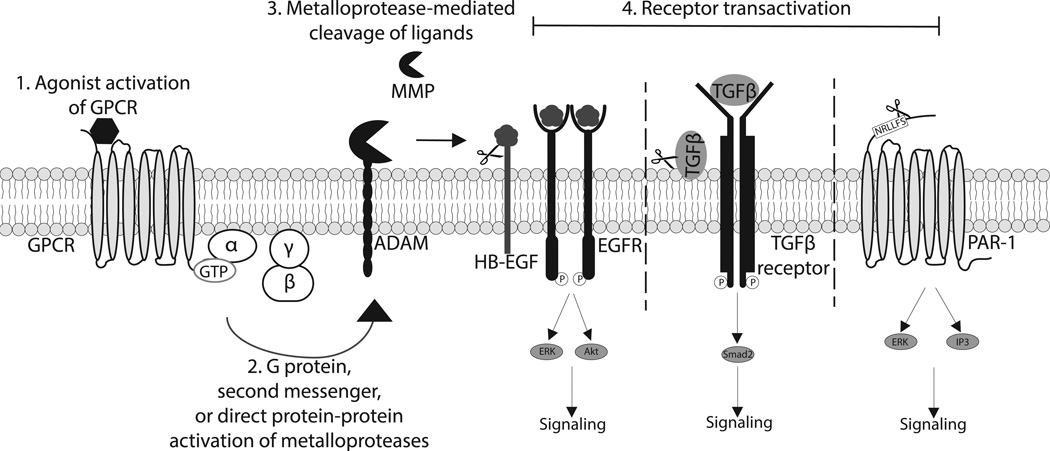
Figure 2. Ligand-dependent mechanism of GPCR-mediated receptor transactivation.
1) Agonist binding of a GPCR leads to activation of heterotrimeric G proteins. 2) Downstream GPCR signaling can lead to activation of ADAMs or MMPs via direct G protein interaction, second messenger activation, or direct protein-protein interaction. 3) Activated ADAMs and MMPs can cleave and release various ligands leading to subsequent 4) receptor transactivation. Activation of EGFR by its ligands, such as HB-EGF, elicits multiple signaling pathways including ERK and Akt activation. Protease release of TGFβ and subsequent activation of the TGFβ receptor leads to canonical signaling through Smad2. Activation of PAR1 via MMP13 leads to ERK1/2 phosphorylation and generation of IP3. MMP13-mediated PAR1 transactivation appears to elicit biased signaling at this receptor, as IP3 generation is decreased compared to canonical agonist, thrombin, stimulation.