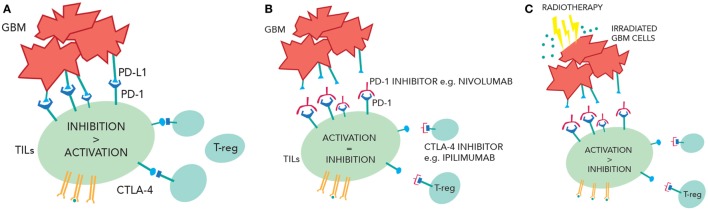
Figure 2.
(A) Inhibition of the tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) due to PD-1/programmed cell death ligand 1(PD-L1) interactions and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) interactions. (B) Checkpoint inhibition of CTLA-4 and PD-1 reduce TIL suppression and increase TIL activity. (C) Radiotherapy releases more tumor antigens causing greater TIL activation. In the context of checkpoint inhibition, this may cause more immune-mediated cell death.