Figure 8.
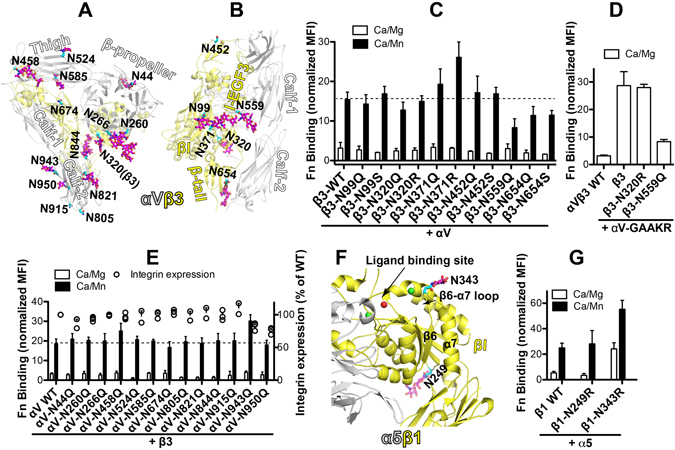
Effect of N-glycan deletions on αVβ3 and α5β1 ligand binding. (A) Locations of αV N-glycan sites in the crystal structure of αVβ3 (PDB code 4G1E). (B) Locations of β3 N-glycan sites in the crystal structure of αVβ3 (PDB code 4G1E). Asn residues are shown as sticks with carbons in cyan. N-glycan residues resolved in the crystal structure are shown as sticks with carbons in magenta. Oxygens and nitrogens are red and blue, respectively. (C) Fibronectin (Fn) binding of HEK293FT-α5β1-KO cells transfected with the β3 WT or the glycan mutants and αV WT. (D) Fn binding of HEK293FT-α5β1-KO cells transfected with the indicated β3 constructs and the αV-GAAKR mutant that mimics integrin inside-out activation. (E) Fn binding of HEK293FT-α5β1-KO cells transfected with the αV WT or the glycan mutants and β3 WT. (F) Locations of selected N-glycans at the βI domain of β1 integrin in the crystal structure of α5β1 headpiece (PDB code 4WJK). Asn and glycans are shown as sticks. Color codes are the same as panels A and B. Metal ions at the ligand-binding site are shown as spheres. (G) Fn binding of HEK293FT-α5β1-KO cells transfected with the β1 WT or the selected glycan mutants and α5 WT. Fn binding was done in the presence of 1 mM Ca2+/Mg2+ (Ca/Mg) or 0.2 mM Ca2+ plus 2 mM Mn2+ (Ca/Mn). Data are means ± s.e.m. (n = 3).
