FIGURE 5.
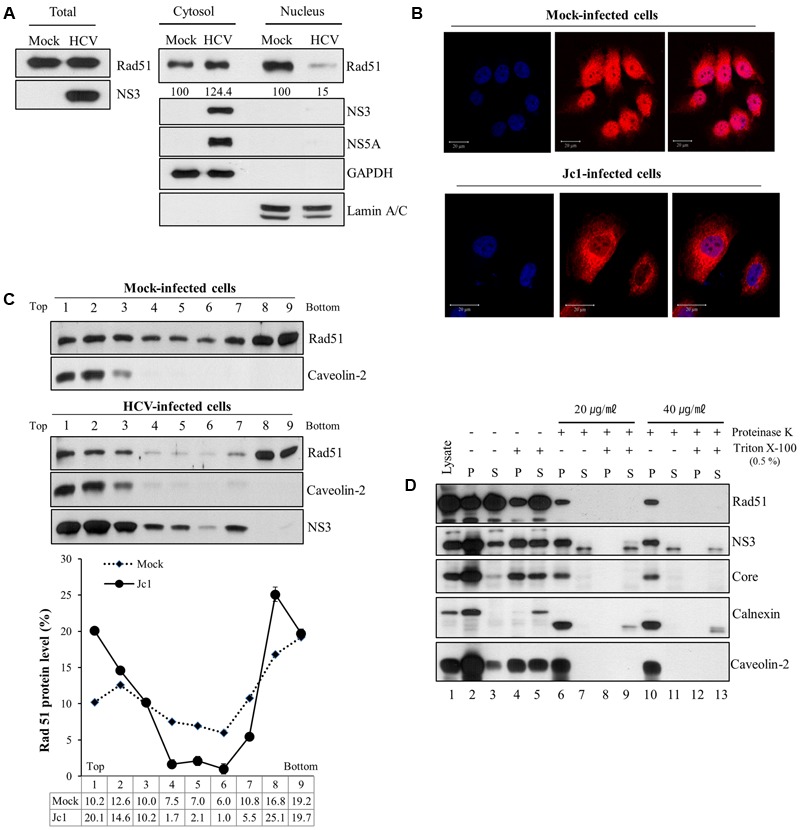
Rad51 is associated with lipid raft. (A) Huh7.5 cells were either mock infected or infected with Jc1 (MOI = 1) for 4 h. At 72 h post-infection, both cytosolic and nuclear fractions were prepared and then protein expression levels were determined by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (B) Huh7.5 cells were either mock-infected or infected with Jc1 for 4 h. At 2 days post-infection, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and immunofluorescence staining was performed by using an anti-Rad51 antibody and TRITC-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG to detect Rad51 (red). Cells were counterstained with DAPI to label nuclei (blue). (C) Huh7.5 cells were either mock- or infected with Jc1 for 4 h. At 72 h post-infection, cells were homogenized and then centrifuged to remove supernatants. The pellets were subjected to membrane floatation centrifugation. (Top panels) Nine fractions were collected and protein levels in each fraction were determined by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (Bottom panel) The band intensities of Rad51 protein in each fraction were quantified using Image J software. (D) Protease protection assay. Post-nuclear supernatants prepared from Huh7.5 cells infected with Jc1 were either left untreated (lanes 2–3), treated with 0.5% Triton X-100 (lanes 4–5), proteinase K (lanes 6–7 and 10–11), or co-treated with Triton X-100 and proteinase K (lanes 8–9 and 12–13). The samples were further centrifuged at 10,000 × g and both pellets (P) and supernatants (S) were determined by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Lane 1, total cell lysate.
