Fig. 6.
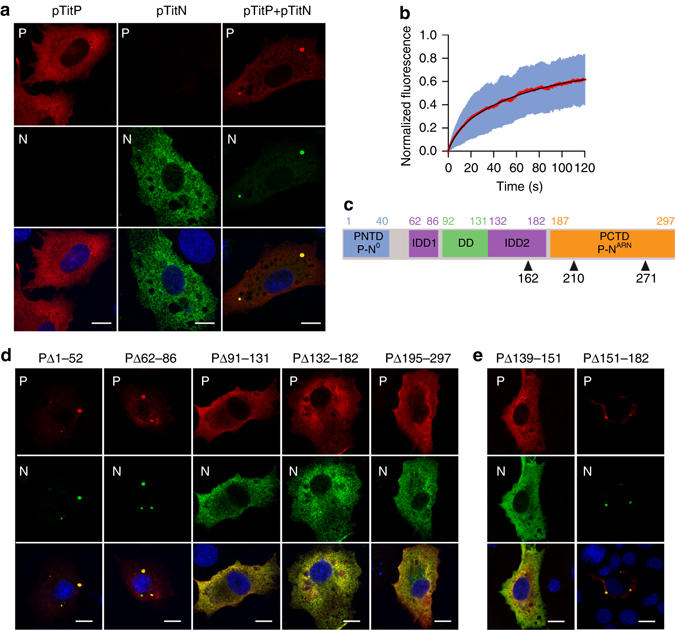
Co-expression of N and P leads to the formation of inclusion bodies recapitulating NB properties. a BSR-T7/5 cells were co-transfected for 24 h with plasmids pTit-P and pTit-N (in equimolar concentration). N was revealed with a mouse monoclonal anti-N antibody followed by incubation with Alexa-488 donkey anti-mouse IgG and P was revealed with a rabbit polyclonal anti-P antibody followed by incubation with Alexa-568 donkey anti-rabbit IgG. DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. Scale bars correspond to 15 µm. b Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) of P-mCherry localized in inclusion bodies in BSR-T7/5 co-expressing P-mCherry and N. The diameter of the photobleached regions was 2.7 µm. FRAP data were corrected for background, normalized to the minimum and maximum intensity, and the mean is shown with error bars representing the SD. Experimental curves were fitted with a two-exponential model (in black). Data were from 21 FRAP events (Supplementary Fig. 6). c Domain organization of RABV P polypeptide chain. P contains an N-terminal domain which binds to N0 (PNTD:P-N0), two intrinsically disordered domains (IDD1 and IDD2), a dimerization domain (DD) and a C-terminal domain which binds to RNA-associated N protein (PCTD:P-NARN). Phosphorylation sites in position 162, 210 and 271 are indicated. d, e Identification of the P domains involved in inclusion bodies formation. BSR-T7/5 cells were co-transfected with plasmids pTit-N and the indicated construction of pTit-P. N was revealed with a mouse monoclonal anti-N antibody followed by incubation with Alexa-488 donkey anti-mouse IgG and P was revealed with a rabbit polyclonal anti-P antibody followed by incubation with Alexa-568 donkey anti-rabbit IgG. DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. Scale bars correspond to 15 µm
