Fig. 7.
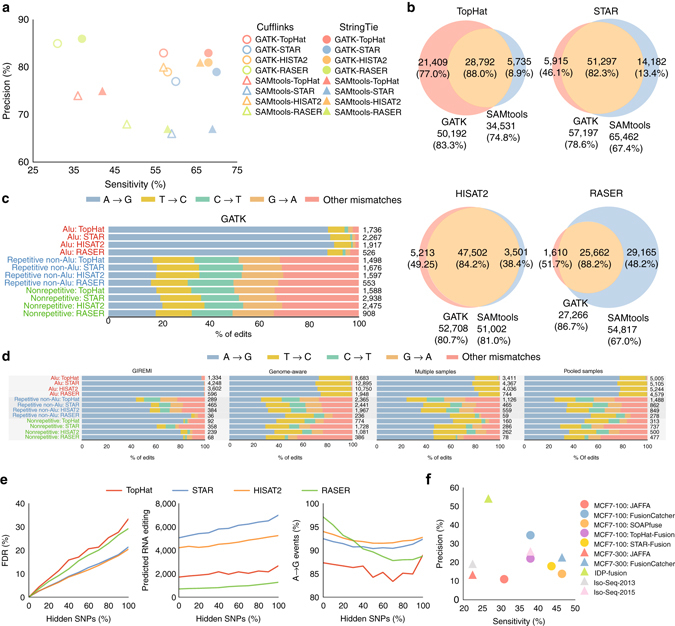
Performance of different variant calling (a–c) RNA editing (d, e) and RNA fusion (f) detection approaches. a Accuracy of detecting NA12878 high-confidence calls in NIST gold standard. The analysis is restricted to the expressed exons identified by Cufflinks or StringTie. b Overlap between variants predicted by GATK and SAMtools. c Distribution of the predicted mismatch types by GATK that are missed in NIST HC calls (in StringTie’s expressed exons) in different genomic regions. d Distribution of RNA editing events detected in different genomic regions for NA12878. For multiple-samples scheme, final editing sites include the rare variants in NA12878 that are supported by at least 3 out of 12 short-read samples in our analysis. For pooled-samples scheme, final editing sites include the rare variants in NA12878 that are supported by at least 20 reads in the pooled alignment. e Measurement of RNA editing detection accuracy when some portion of SNPs are hidden from GIREMI. FDR represent proportion of predicted edits that are among high-confidence genomic variants in NA12878. f Performance of different RNA fusion detection schemes on MCF-7 sample
