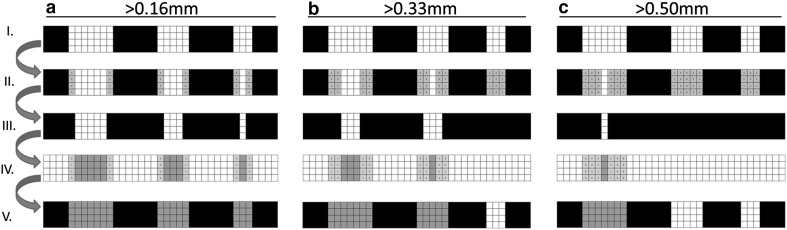
Fig. 1.
Two-dimensional examples of cortical interruptions with different diameters on HR-pQCT voxel level, and the multiple dilation steps that were used to obtain different minimum diameters of interruptions. The following steps are made by the algorithm: (I) shows the original cortex (black) and cortical interruptions (white). The cortex is then dilated with 1 (a), 2 (b) or 3 (c) voxels (II, grey). The dilated cortex (III) is then inverted, and interruptions connected to both the endosteal and periosteal boundary are selected. Finally, the selected interruptions are dilated to its original size (IV), and displayed in the original cortex (V). Shown is that with the increase in the number of dilation steps, only interruptions with a larger diameter are detected (V, green). (Color figure online)