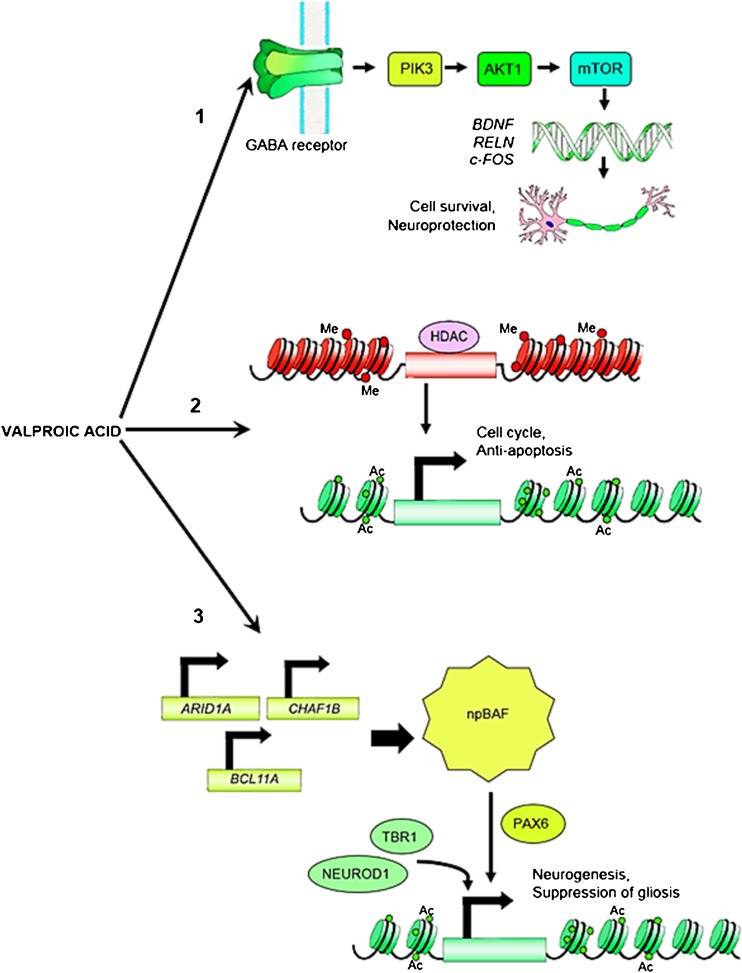
Fig. 7.
Putative mechanisms of VPA in human brain. (1) Activation of AKT1/mTOR signaling pathways by GABA receptors and/or growth factors that activate genes whose expression provides neuroprotection, (2) VPA acts directly to open chromatin through HDAC inhibition, leading to histone acetylation and widespread gene expression including expression of genes involved in the cell cycle, and (3) Chromatin state remodeling complexes such as npBAF containing proteins encoded by ARID1A, BCL11A and CHAF1B, act as intermediaries to prepare for pioneer TFs to initiate neurogenesis and repression of non-neuronal gene expression. There is evidence that PAX6 acts as a pioneer factor in concert with BAF during neurogenesis (61,62). These mechanisms are not mutually exclusive