Figure 9.
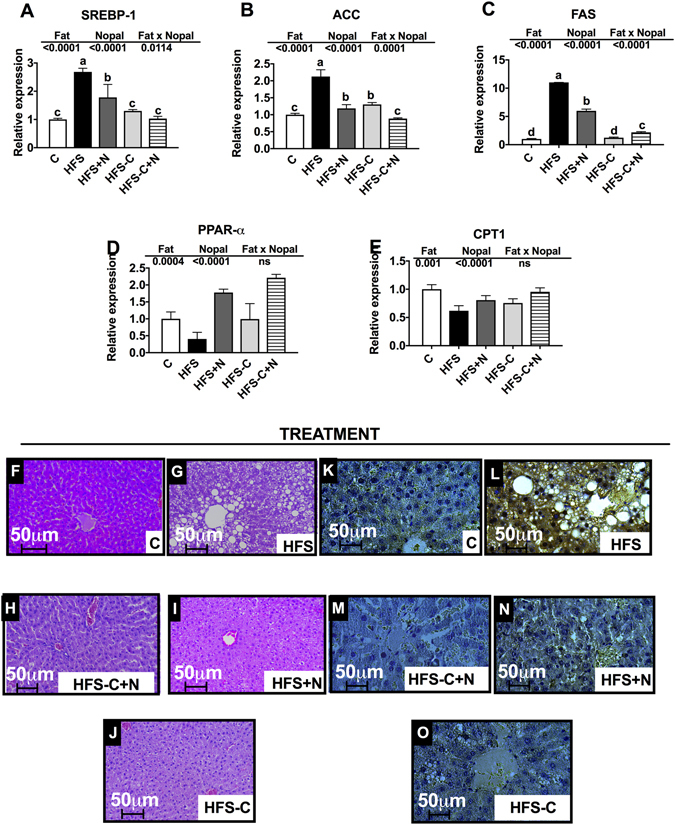
Nopal consumption decreases lipogenesis, hepatic steatosis and inflammation. Relative expression of (A) Srebp-1, (B) Acetyl-CoA carboxylase Acc, (C) Fas, (D) Ppar-α and (E) Cpt-1 in liver of Wistar rats fed one of the following diets: control diet (C), high fat diet with 5% sucrose in drinking water (HFS), HFS + 5% nopal (HFS + N), and obese rats switched to C diet with (HFS-C + N) or without (HFS-C) 5% nopal. (F–J) Hematoxilin-Eosin staining (HE) and (K–O) immunohistochemistry of TNF-α in liver of these rats. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5/group). Comparisons among groups were analysed by 2-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s PLSD test. Different letters indicate significant differences among groups (a > b > c > d). 400X magnification.
