Figure 4.
Overview of Chemical Strategies for Defined Oligoamine Segment Conjugation to Larger Polymer Assemblies
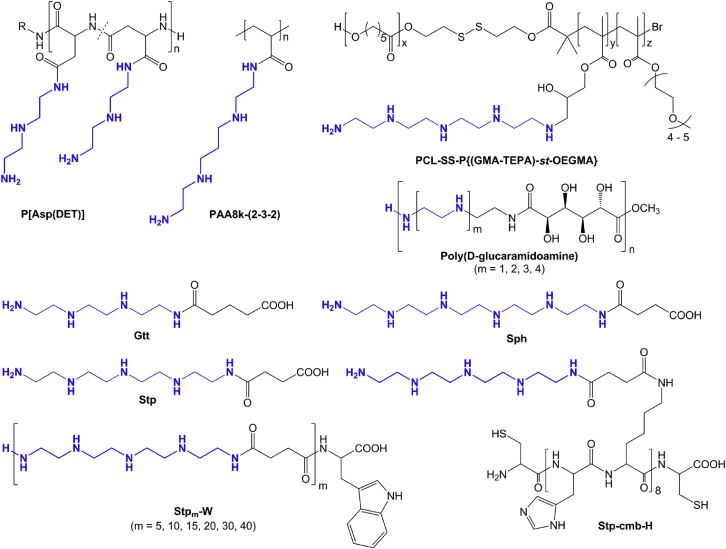
In the illustrated cationic polymers, the polydisperse nature of PEI is dissected into oligoamine segments (blue) with precise size and individual properties. The novel polycationic systems benefit from innovative synthesis techniques producing well defined compounds, possibility of site-specific modification, investigation of detailed structure-activity relationships, and high degree of flexibility. The poly(aspartamide) P[Asp(DET)] is produced by ring-opening N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) polymerization of β-benzyl-L-aspartate N-carboxyanhydride, followed by aminolysis with diethylenetriamine.139, 140, 141, 142 PAA8k-(2-3-2) is synthesized by carbodiimide-mediated amidation of 8-kDa poly(acrylic acid) with N,N′-bis(2-aminoethyl)-1,3-propanediamine.144 PCL-SS-P{(GMA-TEPA)-st-OEGMA} is produced in multiple steps by ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone, atom transfer radical polymerization of glycidyl methacrylate and oligo(ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether methacrylate, and, finally, attachment of tetraethylene pentamine to the polymer scaffold by ring-opening of the reactive epoxy groups.145 Poly(D-glucaramidoamine)s are synthesized by polycondensation of the esterified D-glucaric acid comonomer with the oligoamine segments.146 Gtt, Stp, and Sph represent the deprotected forms of the building blocks used for solid-phase assisted synthesis of sequence-defined oligo(ethanamino) amides.149 Over 1,000 different oligomers with varying structures and topologies have been generated.150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159, 160 Stpm-W represent linear oligo(ethanamino) amides with precise monodisperse size.153 m indicates 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, or 40 repeats of Stp. Stp-cmb-H contains additional histidines for increased endosomal buffering and cysteines for bioreducible cross-link formation.156