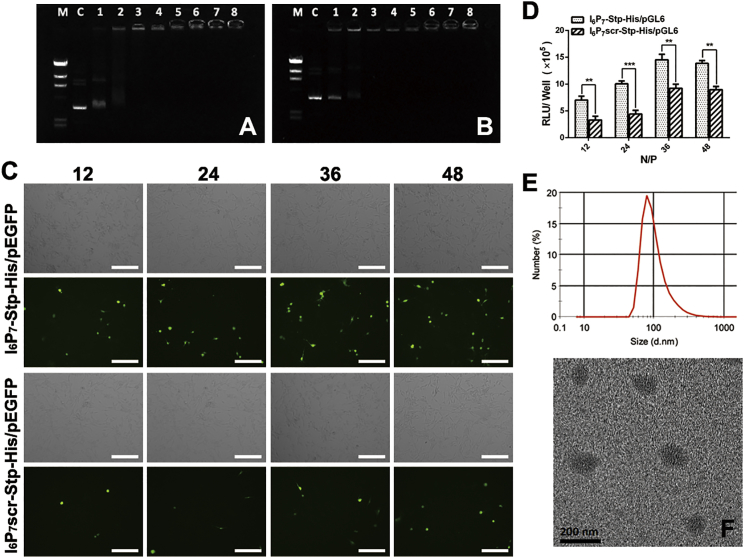
Figure 2.
Optimization and Physical Characterizations of I6P7-Stp-His/DNA and I6P7scr-Stp-His/DNA NPs
DNA binding capacity of I6P7-Stp-His (A) and I6P7scr-Stp-His (B) oligomers was determined by an agarose gel shift assay at a range of N/P ratios. Lane M: DNA marker, Hind III digested; lane C: naked DNA; lane 1: 0.75 (N/P); lane 2: 1.5 (N/P); lane 3: 3 (N/P); lane 4: 6 (N/P); lane 5: 12 (N/P); lane 6: 24 (N/P); lane 7: 36 (N/P); lane 8: 48 (N/P). (C) EGFP gene expression of I6P7-Stp-His/pEGFP and I6P7scr-Stp-His/pEGFP NPs in U87 cells at an N/P ratio of 12, 24, 36, and 48, respectively. Green represents EGFP. (D) Luciferase expression levels of I6P7-Stp-His/pGL6 and I6P7scr-Stp-His/pGL6 NPs in U87 cells at different N/P ratios (12, 24, 36, 48). (E and F) The particle size distribution of I6P7-Stp-His/pGL6 at an N/P ratio of 36 was analyzed by dynamic light scattering (E) and transmission electron microscope (F). Scale bars, 200 μm. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.