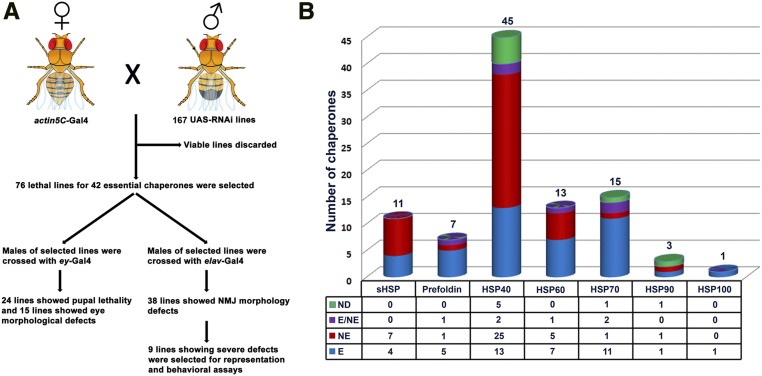
Figure 1.
Workflow for the RNAi screen and list of Drosophila chaperones. (A) Schematic representation of workflow for UAS-RNAi for identification of their neuronal function in Drosophila. A total of 167 RNAi lines corresponding to 95 chaperones were crossed with actin5C-Gal4 for ubiquitous knockdown. The candidate chaperones responsible for lethal events in the F1 generation were considered as essential. All the essential line were then crossed with either ey-Gal4 (to identify chaperones required in eye morphogenesis) or with pan-neuronal elavC155-Gal4 (to identify chaperones required for neuronal function for which NMJ morphology was used as readout). Detailed analysis is shown in Table S1 and Table S2. (B) Histogram showing seven families of chaperones in Drosophila. The number above the histogram represents the total number of chaperones in each family. The Hsp40 family dominated the list, while only one Hsp100 was identified in Drosophila. The table below the histograms shows the number of essential chaperones (E), nonessential chaperones (NE), chaperones for which 50% of lines were lethal (E/NE), and genes for which lines could not be procured (ND). Detailed analysis of actin5C- Gal4 mediated knockdown is shown in Table S1. HSP, heat shock protein; NMJ, neuromuscular junction; RNAi, RNA interference; sHSP, small HSP; UAS, upstream activation sequence.