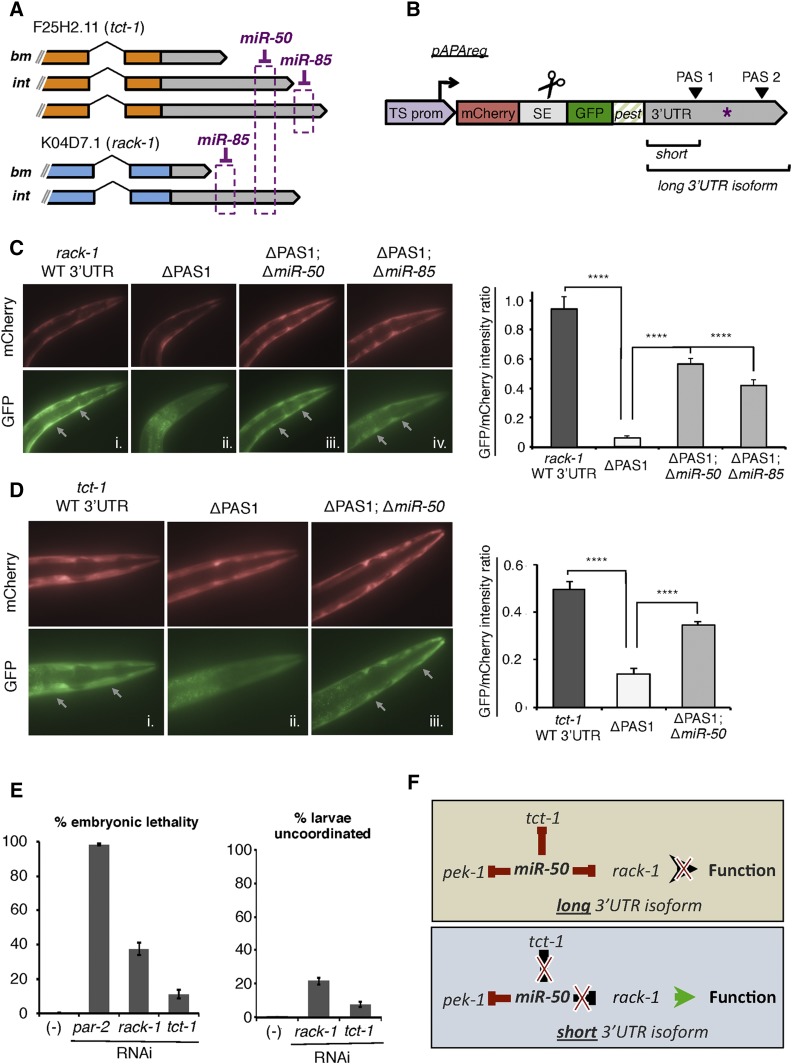
Figure 5.
Tissue-specific APA events allow rack-1 and tct-1 to escape miRNA mediated gene repression in body muscle. (A) Illustration (not to scale) of all 3′UTR isoforms identified in our study for tct-1 (orange) and rack-1 (blue) with the location of PicTar predicted miRNAs targets. We detected their short 3′UTR isoforms in the body muscle (bm) and the long isoforms exclusively in the intestine (int). (B) pAPAreg: A dual-color reporting system to study post-transcriptional gene regulation in vivo. The system uses the Gateway multisite technology. When expressed in C. elegans using tissue-specific promoters, the operon cassette (SE) is cleaved, and both fluorochromes are expressed in the same molar ratio in a given tissue. After the trans-splicing of the spliceable element (SE), the mCherry fluorochrome is translated independently of GFP-PEST, which is instead subject to post-transcriptional repression via miRNAs that target (purple asterisk) in the 3′UTR placed downstream of it. Deletion of PAS1 allows expression of the long 3′UTR isoform containing the miRNA target in the body muscle where it is not normally expressed. (C) rack-1 escapes miR-50 and miR-85 regulation in the body muscle through APA. Left: Representative mCherry and GFP fluorescent images of transgenic lines expressing pAPAreg in the body muscle using the myo-3 promoter and the rack-1 3′UTR with (i) wild-type sequence (WT), (ii) deleted PAS1 (ΔPAS1), (iii) deleted PAS1 and miR-50 target (ΔPAS1;ΔmiR-50), or (iv) deleted PAS1 and miR-85 target (ΔPAS1;ΔmiR-85). Right: Quantification of GFP fluorescence intensity relative to mCherry for each rack-1 transgenic C. elegans line pictured in left panel using Image-J software (n = 34, ****P < 0.0001, paired T-test). (D) tct-1 escapes miR-50 regulation in the body muscle through APA. Left: Representative mCherry and GFP fluorescent images of transgenic C. elegans lines expressing pAPAreg in the body muscle using the myo-3 promoter and the tct-1 3′UTR with (i) wild-type sequence (wt), (ii) deleted PAS1 (ΔPAS1), or (iii) deleted PAS1 and miR-50 target (ΔPAS1;ΔmiR-50). Right: Quantification of GFP fluorescence intensity relative to mCherry for each tct-1 transgenic C. elegans line pictured in left panel using Image-J software (n = 27, ****P < 0.0001, paired T-test). (E) RNAi mediated knockdown of rack-1 and tct-1 results in partial embryonic lethality, (n = 10). C. elegans animals fed rack-1 or tct-1 RNAi exhibit uncoordinated locomotion. Shown are the results from larval C. elegans animals that bypassed embryonic lethality (n = 10). (F) Model depicting the manner in which APA allows rack-1 and tct-1 to escape regulation by the miR-50 miRNA in a tissue-specific manner.