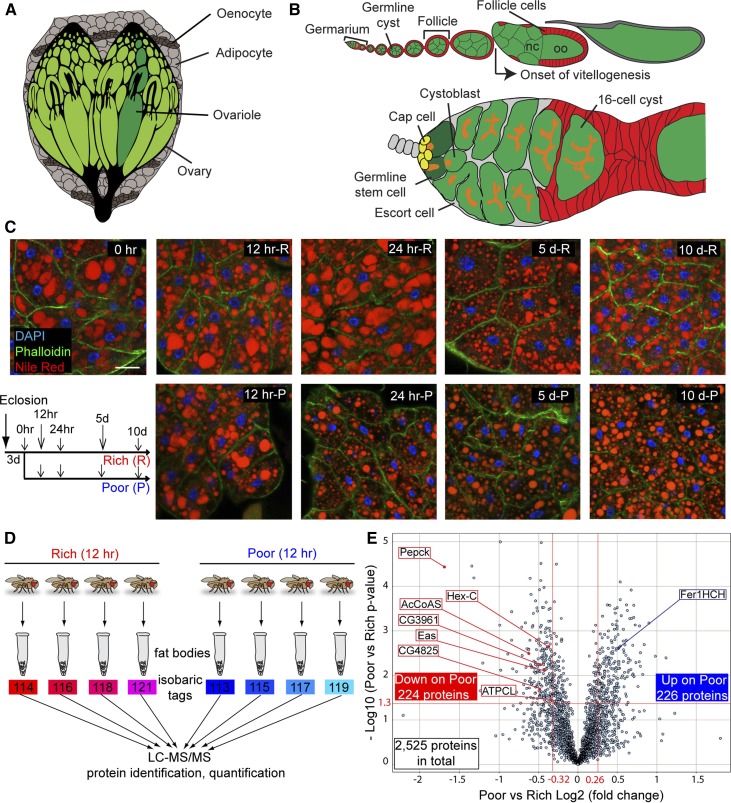
Figure 1.
The fat body proteome undergoes significant changes within 12 hr of dietary switch. (A) The Drosophila fat body, composed of adipocytes and hepatocyte-like oenocytes, surrounds multiple organs. (B) Structure of ovariole (top) and germarium (bottom). Each ovariole contains chronologically arranged follicles, each composed of a 16-cell germline cyst (one oocyte, oo, and 15 nurse cells, nc) enveloped by follicle cells, and vitellogenesis begins at stage 8. Follicles are formed in the germarium, which contains germline stem cells (GSCs) associated with cap cells and a subset of escort cells. Each GSC division produces one GSC and one cystoblast that incompletely divides four times to form a 16-cell cyst. A germline-specific organelle, the fusome (orange), becomes progressively more branched as cysts divide. (C) Adipocyte morphology on different diets. Newly eclosed females were kept for 3 days on a rich diet (R) prior to being switched to a poor diet (P). Control females remained on a rich diet. DAPI (blue), adipocyte nuclei; Nile Red (red), lipid droplets; Phalloidin (green), cell membranes. Scale bar, 40 μm. (D) Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ) flow chart. Four replicates of fat body proteins from females maintained for 12 hr on either rich or poor diets were subjected to iTRAQ analysis. LC-MS/MS, liquid chromatography - tandem mass spectrometry. (E) Volcano plot showing fat body proteins identified by iTRAQ. Proteins with Poor vs. Rich ratio < 0.8 or > 1.2 (red lines at −0.32 and 0.26, respectively, on x-axis) and showing a P-value of < 0.05 by Student’s t-test (red line at 1.3 on y-axis) were considered differentially expressed in response to diet. The x-axis values represent Log2 (Poor to Rich fold change), whereas y-axis values represent −Log10 (Poor vs. Rich P-value). Eight differentially expressed proteins analyzed in this study are indicated. AcCoAS, acetyl-CoA synthase; ATPCL, ATP citrate lyase; CG3961, long-chain acyl-CoA synthase; CG4825, phosphatidylserine synthase 1; Eas, Ethanolamine kinase; Fer1HCH, Ferritin 1 Heavy Chain Homolog; Hex-C, hexokinase-C; Pepck, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase.