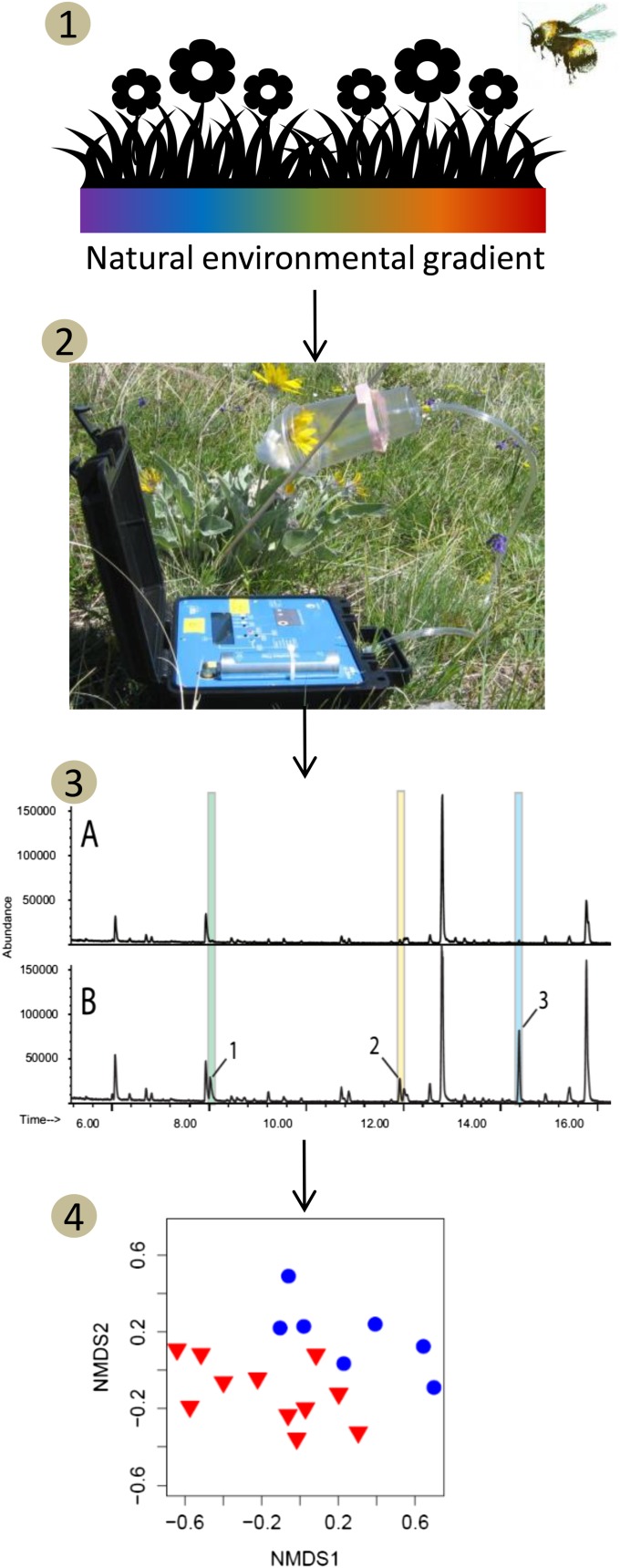
Fig. 1.
Example workflow to investigate how the floral VOCs produced under changing environmental conditions may influence plant–pollinator interactions. (1) Across a natural environmental gradient, or through experimental manipulations of environmental conditions (not shown), measure plant traits and pollinator visitation. (2) Quantify floral VOCs by first enclosing flowers in a container and trapping emitted VOCs on an adsorbent trap using a portable volatile collection system. (3) Then elute, identify, and measure the VOCs using GC-MS. (4) Analyze and visualize patterns in VOCs.