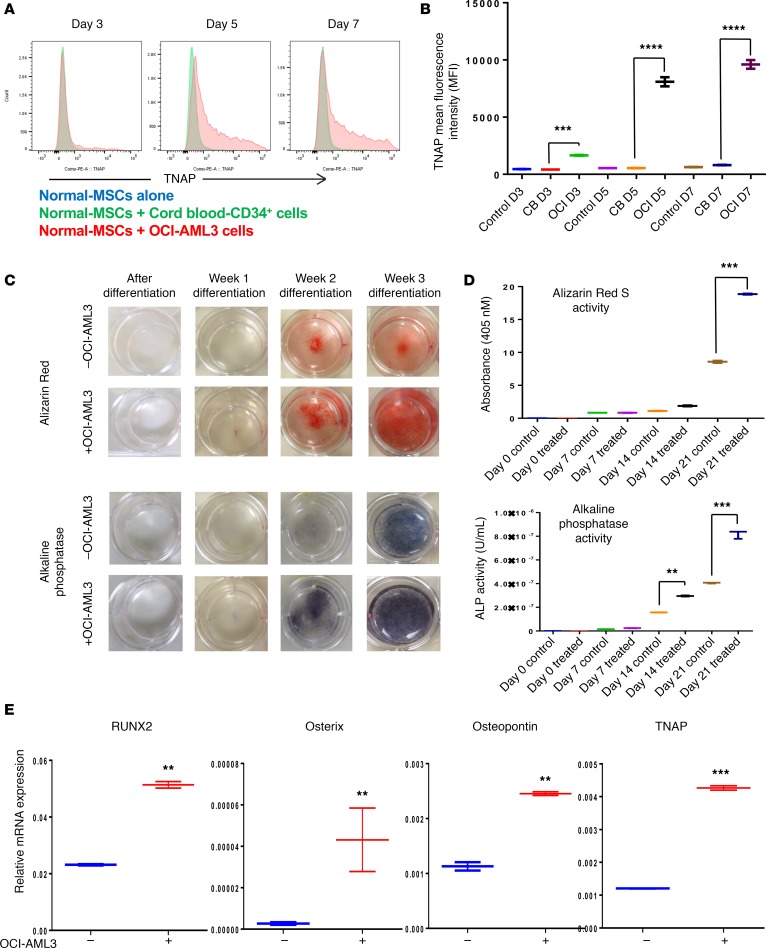
Figure 2. AML cells induce osteogenic differentiation in N-MSCs.
(A) N-MSCs were cocultured with OCI-AML3 cells (red) or with cord blood–derived CD34+ cells (green) or N-MSCs cultured alone (blue) for 3, 5, or 7 days, and TNAP expression was analyzed by LSR-II flow cytometer (n = 3). Data were analyzed and histograms were generated by FlowJo software. (B) MFI of TNAP expression was quantified in N-MSCs cocultured with cord blood–derived CD34+ cells or OCI-AML3 for 3 or 5 days. (C and D) N-MSCs were cultured with or without OCI-AML3 cell–derived conditioned medium (OCI-AML3-CM) for 5 days before long-term (3 weeks) culture in osteogenic differentiation medium. N-MSCs were subjected to Alizarin Red S staining or ALP staining on days 0 (predifferentiation), 7 (week 1), 14 (week 2), and 21 (week 3) of differentiation. (E) mRNAs from N-MSCs cultured with or without OCI-AML3–conditioned medium were examined for expression of indicated osteolineage-associated genes by qRT-PCR (n = 3). GAPDH served as an equal loading control. Two-way ANOVA was used for comparisons of 3 or more groups and unpaired Student’s t test was used for comparisons of 2 groups (** P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 versus control). In addition, Tukey’s multiple comparison test was also performed for the data in B and D.