Figure 1.
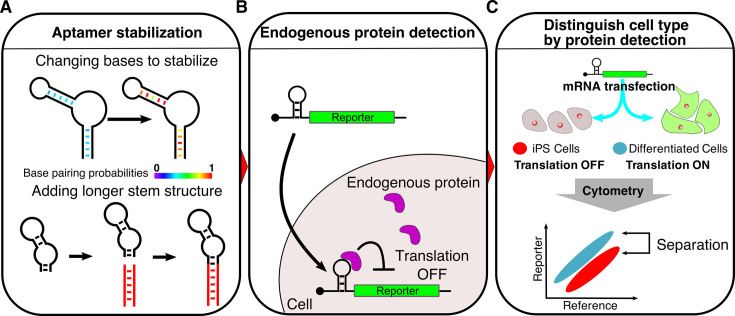
Schematic illustration of detecting endogenous proteins and distinguishing mammalian cells via designed mRNA devices. (A) Stabilization of RNA secondary structures improves the sensitivity of protein-responsive mRNA devices. The RNA devices were stabilized by base-pair substitutions or elongation of the stem structure. Base pairs in red correspond to high base pairing probabilities. Red stems represent additional stem structures. (B) Detection of human endogenous proteins by mRNA devices. The mRNA devices bind to target proteins through RNA–protein interactions in the 5΄-UTR of the mRNA and repress translation of the reporter fluorescent protein, which enables the detection of native target proteins in living cells. (C) Distinction of cell types via mRNA devices. The mRNA-delivered device that responds to a marker protein expressed in human iPS cells can be used to distinguish iPS cells and differentiated cells after analysis of the translation level in each cell type.