Figure 1.
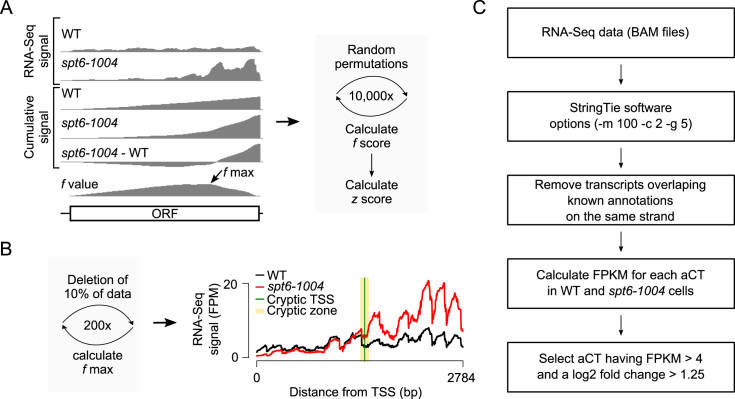
Identification of sense and antisense cryptic transcripts in S. cerevisiae. (A) Schematic representation of the probabilistic method for the identification of genes harboring sense cryptic transcripts. (B) Schematic representation of the probabilistic method for the identification of the cryptic zone and the TSS (left) and the RNA-Seq signal over the CTF4 gene as an example (right). The f max is calculated 200 times, each time by deleting 10% of the data. This allows the determination of a cryptic zone (yellow), a region within the gene where a cryptic transcript is likely to have initiated. The figure also shows the most likely position of the cTSS (green). (C) Workflow of how antisense cryptic transcripts (aCT) were identified in this study.