Figure 6. Schematic of proposed impact of GM3 modulation on IGF1R and Rac1 signaling.
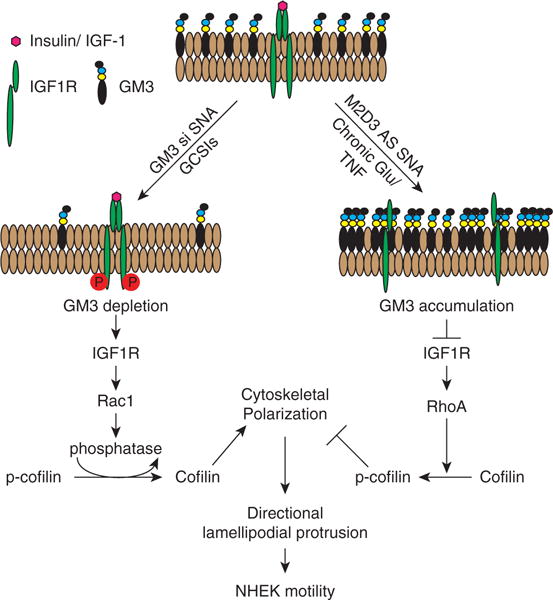
GM3 depletion promotes IGF1R activation, triggering a cascade of phosphorylations that leads to Rac1 activation, cofilin dephosphorylation to polymerize actin, and directional lamellipodial protrusion and increases in both cell velocity and displacement. In contrast, increases in GM3 content suppress IGF1R phosphorylation, leading to RhoA activation, cofilin phosphorylation, and inhibition of cytoskeletal polarization and cell motility. AS, antisense DNA; GCSI, glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; NHEK, normal human epidermal keratinocyte; si, small interfering RNA; SNA, spherical nucleic acid; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
