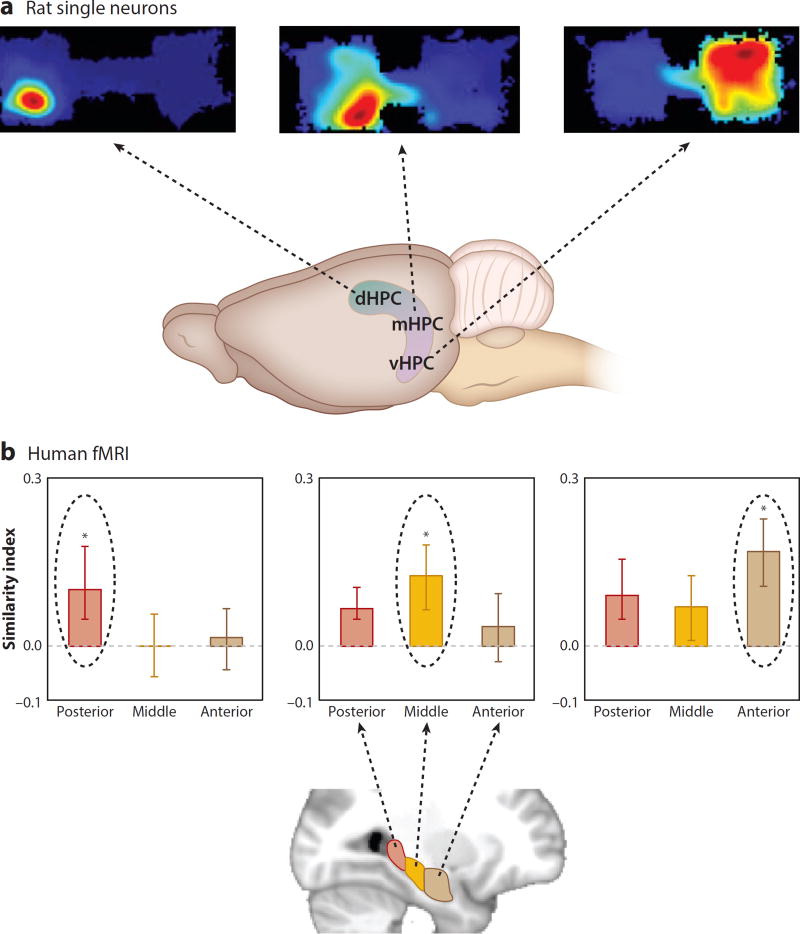
Figure 5.
Topography of specificity and generality of representations along the long axis of the hippocampus. (a) The size of the place fields of hippocampal neurons (as well as the specificity of object and position coding) was graded along the long axis of the hippocampus in rats performing a context-guided object–reward association task. (Top) Outline of the two contexts and a typical place field in each panel. Warmer colors indicate higher firing rates. Blue indicates the area of each context explored. (Bottom) Areas where place fields of different size are found in the dHPC, mHPC, or vHPC. (b) The representational similarities of different scales of association were graded along the long axis of the hippocampus in humans performing an associative inference task. The posterior hippocampus had the highest similarity for one direct association (AB), the middle hippocampus had the highest similarity for both direct associations (AB and BC), and the anterior hippocampus had the highest similarity for the full network of associations (AB, BC, and AC). Panel b adapted with permission from Collin et al. (2015). Abbreviations: dHPC, dorsal hippocampus; mHPC, middle hippocampus; vHPC, ventral hippocampus.