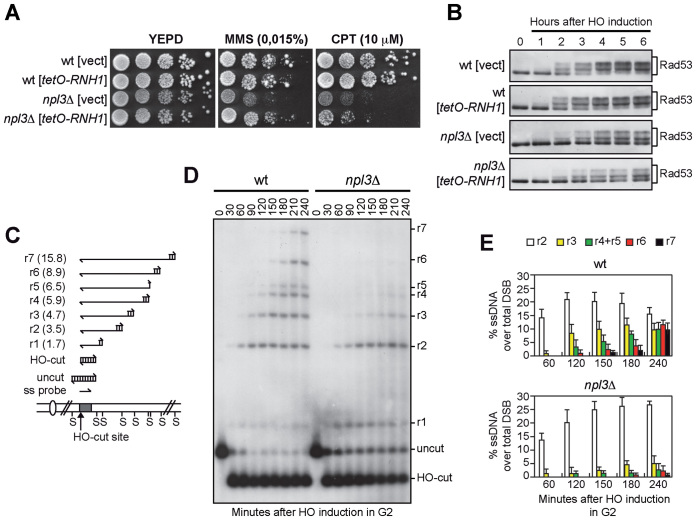
Figure 2.
The lack of NPL3 impairs extensive resection of DSB ends. (A and B) Exponentially growing cell cultures of wild type and npl3Δ strains, both carrying a centromeric plasmid either expressing the RNH1 gene from the tetO promoter or empty (vect), were either serially diluted (1:10) before being spotted out onto YEPD plates with or without MMS or CPT (A), or transferred to YEPRG to monitor Rad53 phosphorylation by western blot (B). (C) System to detect DSB resection. Gel blots of SspI-digested genomic DNA separated on alkaline agarose gel were hybridized with a single-stranded RNA MAT probe (ss probe) that anneals to the unresected strand. 5΄-3΄ resection progressively eliminates SspI sites (S), producing larger SspI fragments (r1 through r7) detected by the probe. (D and E) Exponentially growing YEPR cell cultures were arrested in G2 with nocodazole and transferred to YEPRG (time zero) in the presence of nocodazole. (D) DSB resection as described in (C). (E) Resection products in (D) were analyzed by densitometry. The mean values are represented with error bars denoting SD (n = 5).