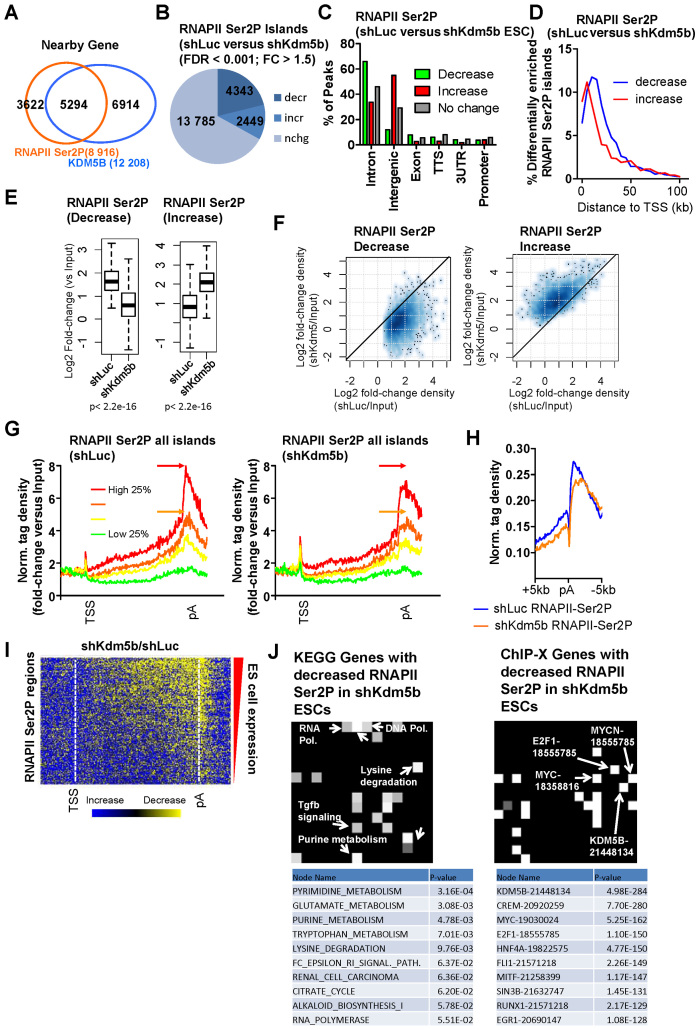
Figure 4.
KDM5B regulates RNAPII elongation in ES cells. (A) Venn diagram showing overlap of RNAPII-Ser2P and KDM5B in gene body regions in ES cells. (B) Change in the global distribution of RNAPII-Ser2P in shKdm5b versus shLuc ES cells as defined by SICER analysis (see methods, fold-change > 1.5, FDR < 0.001). (C) Annotation of differentially enriched RNAPII-Ser2P regions shLuc and shKdm5b ES using HOMER software (34). (D) Histogram showing the distance of differentially enriched (increased or decreased) RNAPII Ser2P islands from TSS regions. Note that RNAPII Ser2P islands with decreased levels are located further from TSS regions relative to islands with increased levels. (E) Boxplots and (F) scatter plots of RNAPII-Ser2P densities in shLuc and shKdm5b ES cells. (G) Average profile of RNAPII-Ser2P binding normalized by input (log2 fold-change versus Input) at all refseq genes (TSS-TES) sorted into quartiles based on their expression level in control (shLuc) ES cells. The red and orange arrows denote the peak of RNAPII Ser2P in shLuc ES cells. (H) Average profile of RNAPII-Ser2P density at TES regions in shLuc and shKdm5b ES cells. RNAPII-Ser2P is known to be enriched at TES regions of genes. (I) Heat map of change in RNAPII-Ser2P in shKdm5b versus shLuc ES cells (yellow, decrease). (J) KEGG gene (left heatmap) and ChIP-X genes (right heatmap) evaluated using Network2Canvas demonstrates that metabolic and lysine degradation genes have decreased RNAPII-Ser2P in shKdm5b ES cells, and are bound by KDM5B. Each node (square) represents a gene list (shLuc versus shKdm5b bound genes bound by RNAPII-Ser2P associated with a gene-set library (KEGG or ChIP-X). The brightness (white) of each node is determined by its P-value.