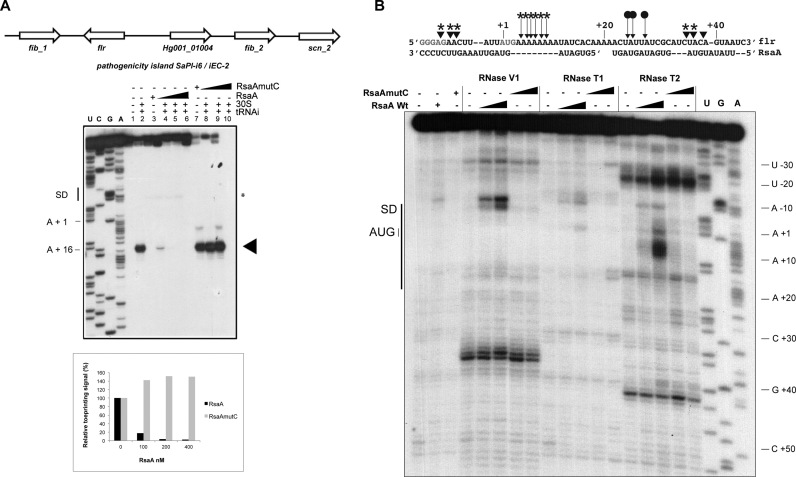
Figure 5.
Characterization of the inhibitory RsaA–flr mRNA complex. (A) Genetic organization of the pathogenic island containing the flr gene and effect of RsaA on the formation of initiation ribosomal complex on flr mRNA (50 nM). Lane 1: incubation control of mRNA; lane 2: formation of the ribosomal initiation complex containing mRNA, the 30S subunits and tRNAfMet (tRNAi); lane 3: incubation control of mRNA with WT RsaA ; lane 4–6: formation of the initiation complex in presence of increasing concentrations of WT RsaA : 100, 200, 400 nM. lane 7: incubation control of mRNA with RsaAmutC; lanes 8–10: formation of the initiation complex in the presence of increasing concentrations of RsaAmutC: 100, 200, 400 nM. Lanes U, A, G, C: sequencing ladders. The SD sequence, the start site of translation (A +1 of the AUG initiation codon) and the toe-printing signals (N +16) are indicated. * indicates the RT stop induced by RsaA binding on flr mRNA. Graph showing the quantification of the toe-print signals. The toe-print signals with flr mRNA in the presence of increasing concentrations of RsaA or RsaAmutC were normalized according to the total amount of radioactivity (full-length extension and +16 product bands) using the ImageQuanTL software (GE Healthcare). (B) Footprinting assays to map RsaA–flr mRNA interactions. Enzymatic reactions performed on flr mRNA free or bound to either RsaA or RsaAmutC (25 and 50 nM). The first three lanes represent incubation controls of free mRNA, bound to RsaA WT or RsaAmutC, respectively. Lanes T, G, A: dideoxy sequencing reactions. The experiments were performed with RNase V1 (V1), RNase T1 (T1) and RNase T2 (T2). On the sequence of flr mRNA are shown the RNase cleavages, which have been reproducibly found in two independent experiments: triangles denote RNase V1 cuts, filled arrows denote RNase T2 cuts. Effect of RsaA binding: protections are given by circles and enhanced or new RNase V1/T2 cleavages are labelled by stars.