Figure 7.
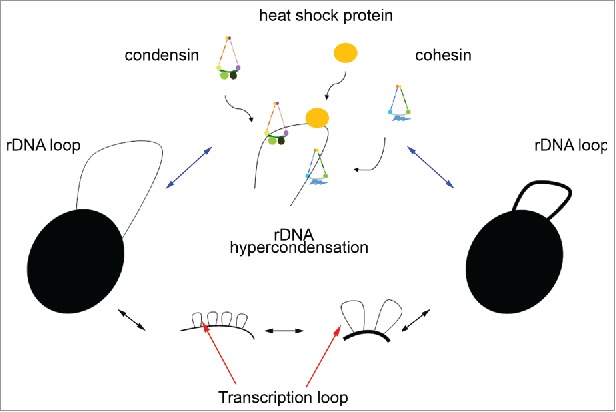
Model of rDNA transcription loop extension and possible mechanisms of hypercondensation. rDNA hypercondensation occurs in cells exposed to elevated temperature, potentially through transcription-dependent increase in axial loop extension (below). Candidates required to drive mitotic hypercondensation may include temperature-dependent enhanced activation of cohesin, condensin, or heat shock proteins (either directly or through condensation inhibitor inactivation) that specifically target the rDNA loci (above).
