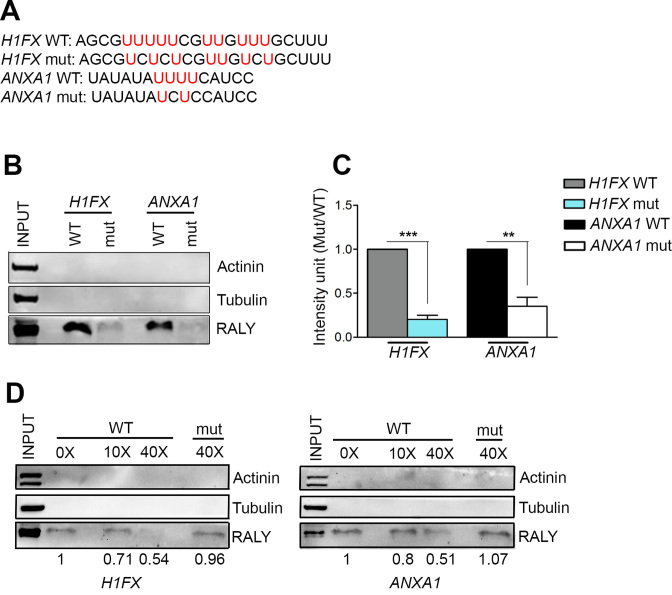
Figure 7.
RALY binds the poly-U regions. (A) Sequences of biotinylated wild-type and mutant H1FX and ANXA1 3΄UTR probes. (B) MCF7 cells total protein extract was incubated with either wild-type or mutant biotinylated RNA probes (50 pmol) and captured by streptavidin beads. Western blot of RNA-bound protein fraction shows the positive interaction in vitro of RALY with the poly-U wild-type sequences, but not with mutant probes. Immunoblotting with anti-Actinin and anti-Tubulin served as a negative control. (B) The graphs show the mean values of three independent experiments. Bars represent mean ± S.E.M. P-value was calculated by unpaired two-tailed t-test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). (C) RNA pull-down competition assay was performed to assess the RNA-binding specificity of RALY. 30 pmol of either H1FX or ANXA1 wild-type probes were incubated with increasing amounts (10× and 40×, respectively) of non-biotinylated wild-type or 40× mutant probes and successively mixed with 30 μg of MCF7 cells extract. Western blot shows the amount of RALY bound to the probes in the different competitive conditions and quantified by band densitometry analysis. Immunoblotting with anti-Actinin and anti-Tubulin served as a negative control.