Figure 2.
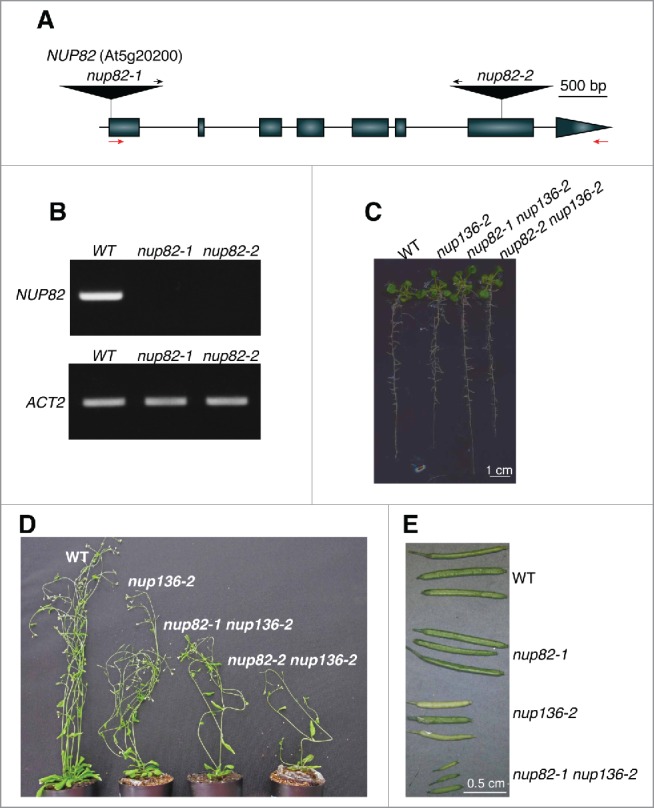
Isolation of nup82 nup136 double mutants. (A) A schematic representation of the NUP82 gene, which contains 8 exons. The positions of T-DNA insertions in nup82–1 and nup82–2 are shown. Closed boxes and solid lines indicate exons and introns, respectively. Black arrows indicate the orientation of the left border sequence. Red arrows indicate the primers used for RT-PCR in (B). (B) RT-PCR analysis of NUP82 and ACTIN2 (ACT2) transcripts in the wild-type (WT), nup82–1, and nup82–2. Amplification of NUP82 and ACT2 required 40 and 27 PCR cycles, respectively. These data are representative of 2 biologic replicates and 2 technical replicates. (C) Thirteen-day-old seedlings of wild-type (WT), nup136–2, nup136–2 nup82–1, and nup136–2 nup82–2 plants. (D) Five-week-old wild-type (WT), nup136–2, nup136–2 nup82–1, and nup136–2 nup82–2 plants. (E) Siliques of wild-type (WT), nup82–1, nup136–2, and nup136–2 nup82–1 plants.
