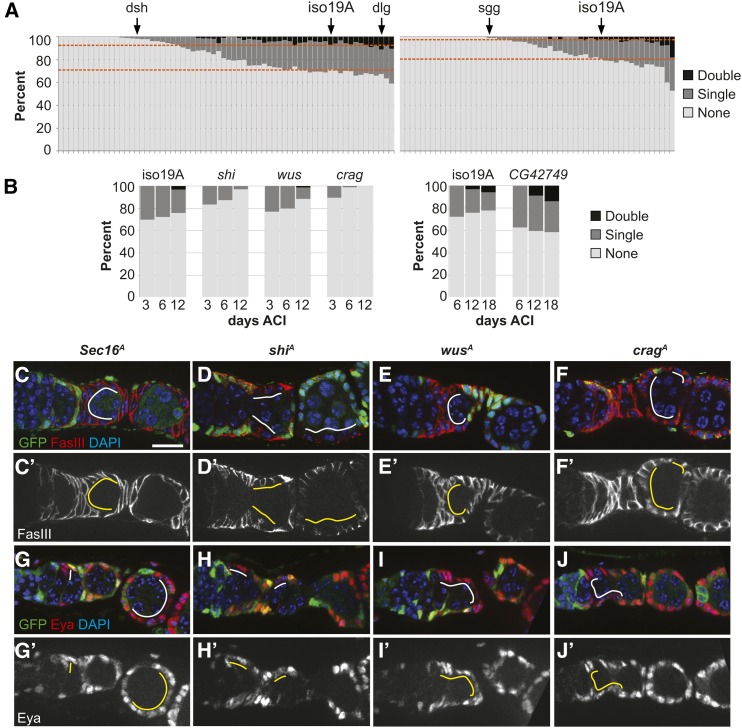
Figure 2.
(A) Screen results. Dashed lines represent the “double”/“single” border and “single”/“none” border for the isoFRT19A control in each set. (B) Niche competition assays for four candidate alleles identified in the first part of the screen. Consistent with the predictions from the primary screen, the Crag, shi, and wus alleles cause a decrease in FSC clone frequency, and the CG42749 allele causes an increase in clone frequency. (C–J and C′-J′) GFP− Sec16A, shiA, wusA, and CragA FSC clones 6 days ACI stained for follicle cell markers (C–F) FasIII or (G–J) Eya (red), GFP (clonal marker, green), and DAPI (blue). Position of mutant follicle cells indicated by solid white and yellow lines. Mutant clones grow, form a single layered epithelium around the germ cell cysts, and express FasIII and Eya. Bar, ∼10 μm.