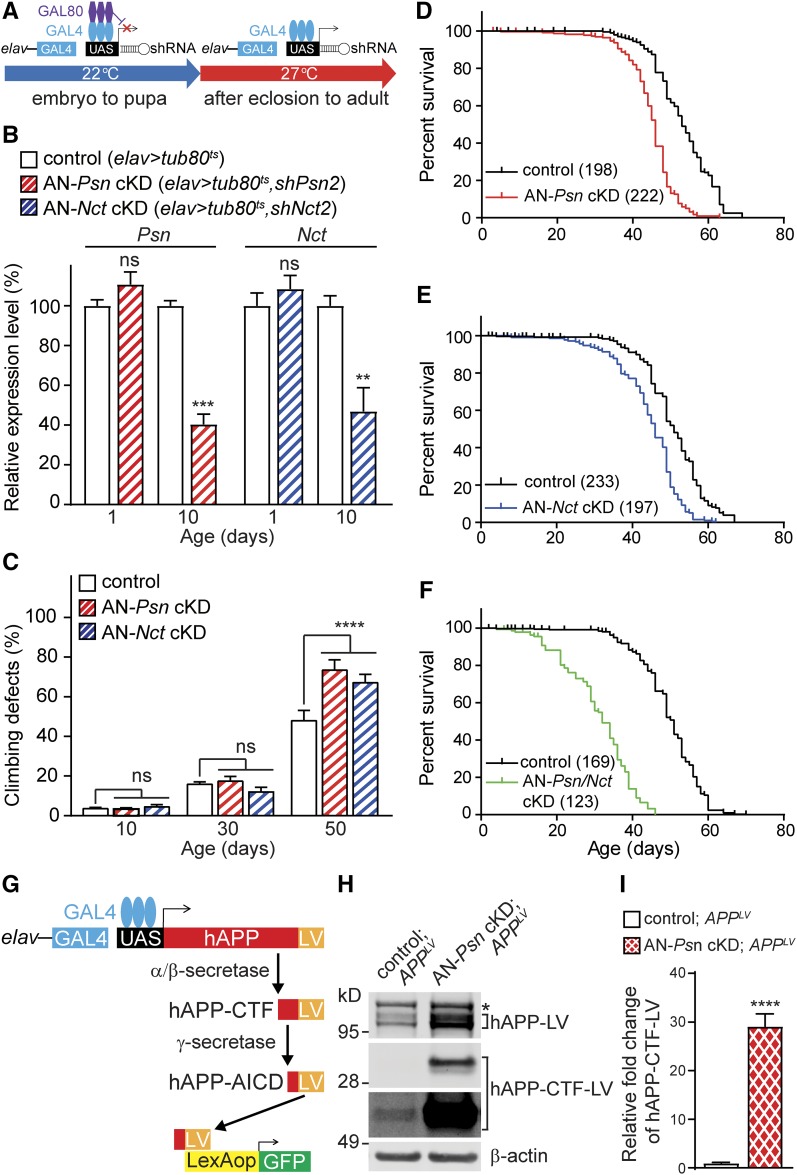
Figure 7.
Age-dependent climbing defects and shortened lifespan in adult neuron-specific Psn and Nct KD flies. (A) Strategy for imposing temporal control of shRNA expression using Gal80ts. (B) Adult neuron-specific conditional KD of Psn (AN-Psn cKD; red) and Nct (AN-Nct cKD; blue) results in significant reduction of Psn (red) or Nct (blue) mRNA level in 10-day-old male fly heads, but no significant difference in 1-day-old male fly heads compared to control. qRT-PCR analysis of Psn and Nct mRNA level in the male adult heads of 1 and 10 day-old flies. Total RNA was extracted from 20 male adult heads. Psn and Nct mRNA levels were normalized to rp49 mRNA levels as internal control. n = 4 independent experiments. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc comparisons. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C) Adult neuron-specific Psn or Nct KD causes defects in climbing ability at the age of 50 days. Bar indicates percentage of failed climbers. n ≥ 5 independent experiments, ≥100 flies per genotype (20 flies per experiment). All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc comparisons. Two-way ANOVA showed main effects of genotype [F(2, 45) = 6.471; P = 0.0034] and age [F(2, 45) = 556.1; P < 0.0001] with an interaction between these factors [F(4, 45) = 9.905; P < 0.0001]. ns, nonsignificant; ****P < 0.0001. (D–F) Adult neuron-specific Psn and Nct cKD reduce lifespan. AN-Psn/Nct cKD flies showed a greater reduced lifespan relative to AN-Psn cKD and AN-Nct cKD flies. Survival of control (black), AN-Psn cKD (red, D), AN-Nct cKD (blue, E), and AN-Psn/Nct cKD (green, F). Lifespans were plotted by the Kaplan-Meier method. (G–I) Impairment of γ-secretase activity in AN-Psn cDK flies. (G) Strategy for assessing γ-secretase dependent cleavage of the APP-LV reporter system. (H) Western analysis shows dramatic increases of γ-secretase substrate hAPP-CTF-LV in the adult head of male AN-Psn cKD; APPLV flies, indicating reduction of γ-secretase activity. β-actin was used as loading control. Asterisk marks nonspecific band. (I) Quantification of hAPP-CTF-LV levels in AN-Psn cKD; APPLV and control fly heads. hAPP-CTF-LV levels were normalized to β-actin and full length APP protein; n = 3 independent experiments. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired Student’s t-test. ****P < 0.0001.