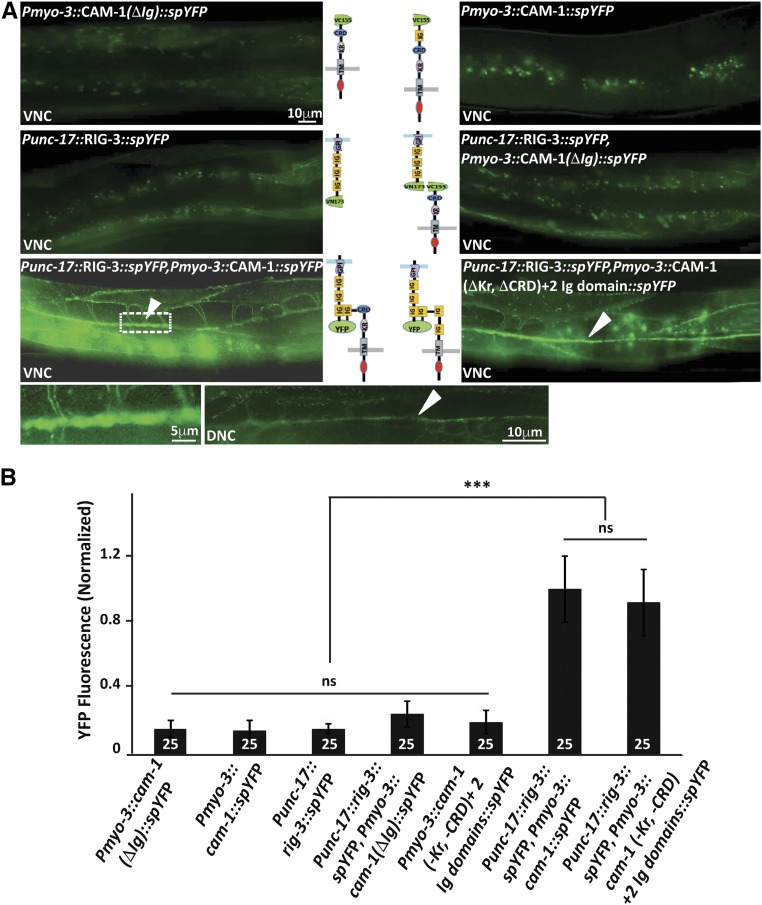
Figure 2.
RIG-3 directly interacts with CAM-1. (A) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) analysis of CAM-1 and RIG-3 interaction at the NMJ: the figure shows representative fluorescent images (YFP) of the C. elegans Dorsal Nerve Cord (DNC) expressing the transgenic protein indicated. The top four panels display the controls showing basal YFP levels with Pmyo-3::CAM-1(ΔIg)::VC155, Pmyo-3::CAM-1(FL)::VC155, Punc-17::RIG-3::VN173, and Punc-17::RIG-3::VN173 coinjected with Pmyo-3::CAM-1(ΔIg)::VC155. The lower two panels that are adjacent to the illustrations of the constructs used in the BiFC experiments show the image where Punc-17::RIG-3::VN173 is coinjected with Pmyo-3::CAM-1(FL)::VC155 and Punc-17::RIG-3::VN173 is coinjected with Pmyo-3::CAM-1(ΔKr, ΔCRD)+ 2Ig::VC155 respectively. A clear increase over the basal levels of YFP is seen in these panels. The image to the bottom right of the figure is a small area along the VNC that has been zoomed into from the image on the left (dotted box). The image next to it shows expression of YFP along the DNC in the same animals that show YFP expression in the VNC, this was seen in all eight animals that were assayed to look at the DNC. VNC indicates ventral nerve cord, and DNC indicates dorsal nerve cord, respectively. CAM-1 was expressed in the body-wall muscle with the myo-3 promoter, while RIG-3 was expressed in cholinergic neurons using the unc-17 promoter. (B) Graph of the bimolecular fluorescence images: In order to quantify the YFP fluorescence levels, 25 animals for each genotype where imaged, and their fluorescence along the ventral nerve cord quantified and plotted in the graph. The fluorescence intensity was normalized against C. elegans coexpressing Punc-17::RIG-3::VN173 and Pmyo-3::CAM-1(FL)::VC155. Error bars indicate SEM.