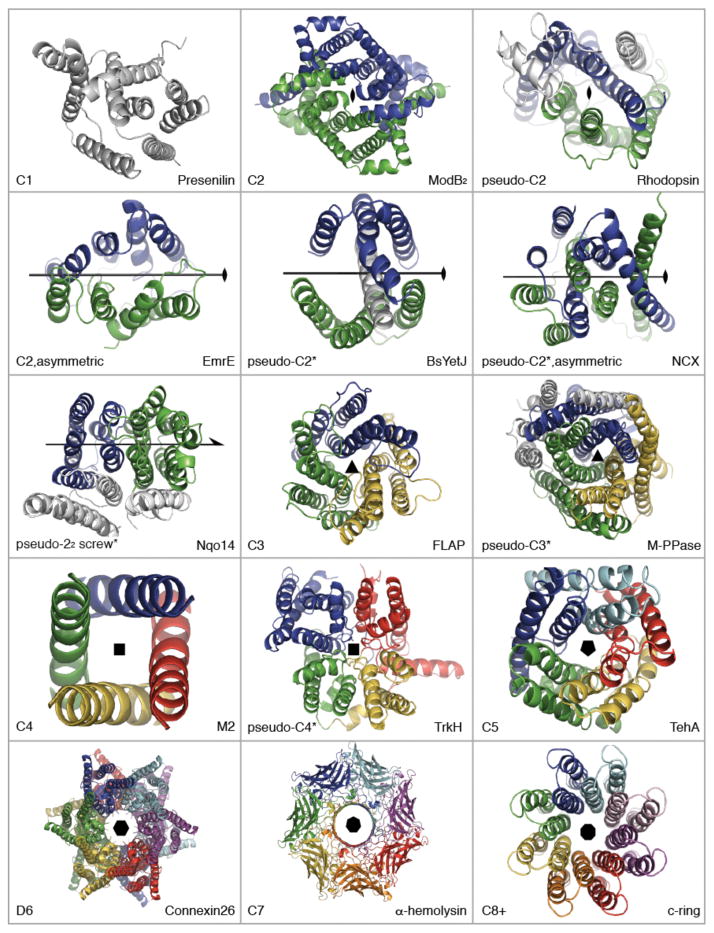
Figure 2.
Point symmetry types in membrane protein structures. Structures are shown as cartoon helices, viewed down onto the membrane. Different colors are used to indicate symmetric elements, i.e., independent chains or (*)internal repeats. Non-symmetric elements are in gray. EmrE is an asymmetric homo-dimer (PDB entry: 3B5D), while other transporters are asymmetric as well as pseudo-symmetric (e.g., NCX, 3V5U). Two-fold screw axis (22)-pseudo-symmetry is seen in the Mrp antiporter-like subunits of complex I (see Figure 4). Presenilin is an aspartate protease (4HYG). ModB2 is from the homodimeric molybdate type I ABC importer (2ONK). MalFG is from the heterodimeric MalFGK2 type I ABC importer (2R6G). BsYetJ is a pH-dependent Ca2+ channel from the TM Bax inhibitor motif (TMBIM) family (4PGW). FLAP, or five-lipooxygenase-activating protein, is a member of the family of membrane-associated proteins in eicosanoid and glutathione metabolism (MAPEG, 2Q7M). M-PPase is a membrane pyrophosphatase (4AV3). M2 is a H+ channel from influenza A (3LBW, TM domains only). TrkH is a K+ channel from the superfamily of K+ transporters (SKT, 3PJZ). TehA is a SLAC anion channel homolog (3M73 chain A). Connexin-26 is a gap junction (2ZW3); each hemi-channel exhibits C6 symmetry. α-hemolysin is a pore-forming toxin (7AHL). The c8-ring is a F-type ATP synthase membrane rotor (2XND). Symmetry axes were defined using SymD v1.3 (52) and figures were made with Pymol v1.7 (Schrödinger Ltd).