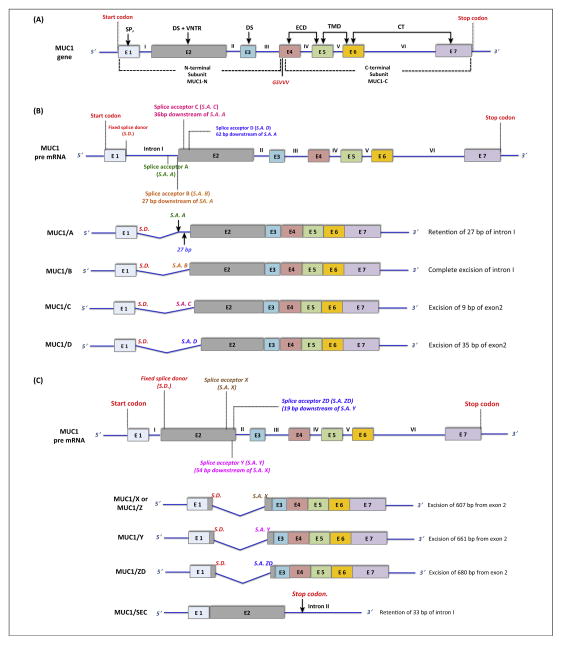
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the MUC1 gene and the different isoforms of MUC1. (A) The MUC1 gene consists of seven exons (E1 to E7, indicated by different colored boxes) and six introns (I to VI, blue lines). Exons 1–3 encode the MUC1 N-terminal and exons 4–7 encode the MUC1 C-terminal subunits. Exons encoding the corresponding domains are indicated by an arrow. Exon 1 (E1) encodes the signal peptide (SP), E2 encodes the N-terminal degenerate sequence (DS) and the VNTR, and E3 encodes the C-terminal DS. E4, E5, E6, and E7 together encode the extracellular domain (ECD), transmembrane domain (TMD), and cytoplasmic tail (CT). MUC1 is encoded as a single polypeptide chain that undergoes spontaneous cleavage at the GSVVV site (red) to generate the MUC1-N and MUC1-C subunits. (B) MUC1 pre-mRNA is spliced into four main variants of mature MUC1 mRNA – MUC1/A, MUC1/B, MUC1/C, and MUC1/D, all encoding ‘full-length’ MUC1. These isoforms are generated by alternative splicing between the fixed splice donor site near the 5′ end of intron I (red) and multiple splice acceptor sites near the 3′ and 5′ end of intron I and exon II, respectively (green, orange, magenta, and blue). In MUC1/A, a portion of the intron I (27 bp) is retained, coding an alternative signal peptide without causing a reading frameshift. In MUC1/B, intron I is completely removed. Portions of exon 2 are spliced out while retaining the reading frame in MUC1/C and MUC1/D, resulting in shorter VNTRs [31]. (C) MUC1 mRNA also contains a cryptic intron in exon 2. Several alternative splice acceptor sites around the 3′ end of exon 2 (brown, magenta, blue) can link with the fixed splice donor site at the 5′ end of exon 2 (red). Splicing between these sites results in the formation of the splice variants MUC1/X (or MUC1/Z), MUC1/Y, and MUC1/ZD, which completely lack the VNTR region. MUC1/SEC, the secreted isoform, is generated by a failure to excise intron 2, leading to premature abortion of transcription caused by the presence of a stop codon within intron 2 [112,113]. Abbreviations: MUC1, Mucin 1; E, exon; VNTR, variable number tandem repeat; MUC1-N, MUC1 N-terminal; MUC1-C, MUC1 C-terminal; S.D., splice donor; S.A., splice acceptor.