Figure 1. SSRP1 maintains cell survival after ionizing radiation (IR) and methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) treatments.
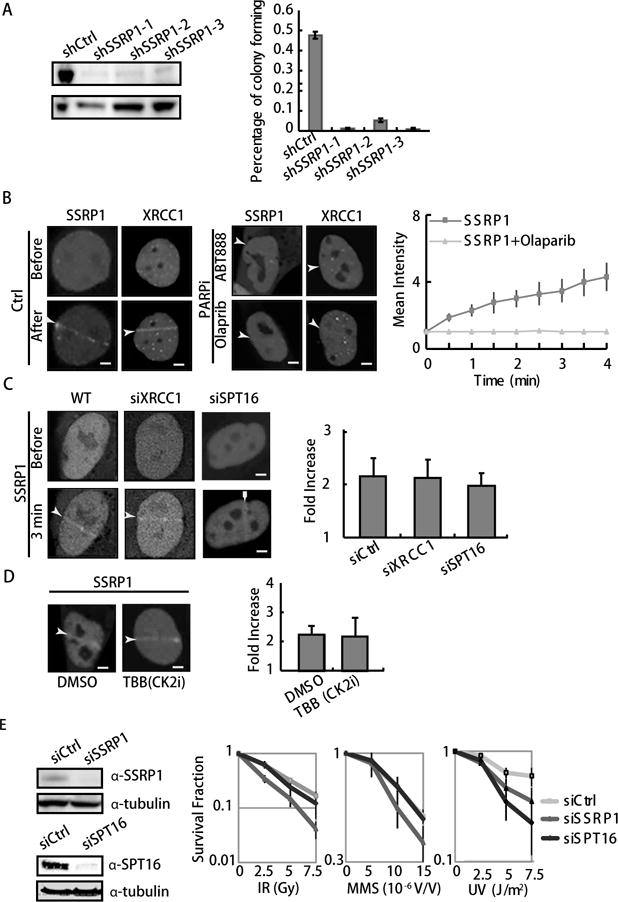
A. Suppression of SSRP1 by shRNA 1–3 is shown by WB (left panel). The colony-forming ability of the SSRP1 suppressed cells is shown by the percentage of colonies formed in 350 cells. Error bars are derived from SEMs in three repeated experiments (right panel). B. Accumulation of GFP-tagged XRCC1 and SSRP1 at sites of damage before and after 100 ms laser micro-irradiation in U2OS cells (left and middle panels). Cells were pretreated with ABT888 or olaparib for 30 min, then imaged (lower panels). PARP inhibitors suppress the accumulation of GFP-tagged SSRP1 at sites of damage. Kinetics of GFP-SSRP1 after laser micro-irradiation with and without PARPi in U2OS cells. The relative intensity vs. background is shown as a fold intensity, which was obtained from the mean damage site/background intensity. Error bars were derived from SDs in three independent experiments (right panel). C–D. Repression of SPT16, XRCC1 or CK2 phosphorylation does not inhibit the recruitment of SSRP1 at laser induced damage sites. Accumulation of GFP-tagged SSRP is shown at sites of damage 3 min after 100 ms laser micro-irradiation in U2OS cells. The cells used were either knocked down w/o siXRCC1 or siSPT16 (C), or pretreated with a CK2 inhibitor, TBB (D). Fold increase of intensity is shown. E. Clonogenic survival assay in SSRP1 or SPT16 suppressed HeLa cells by siRNA. Cells were pretreated with IR, MMS or UVC, and further incubated for 9 days before staining with 0.3% of crystal violet/methanol for the assay. For Western blot (WB), HeLa cells 48 h after treatment with siRNA for SSRP1 and SPT16 (left panel). For IR and UVC, cells were treated with the indicated dose 8 h after passaging. Suppression of SSRP1 but not SRP16 significantly sensitizes cells to IR and MMS treatment. Error bars are derived from SDs in three independent experiments (right Panel).
