Figure 5.
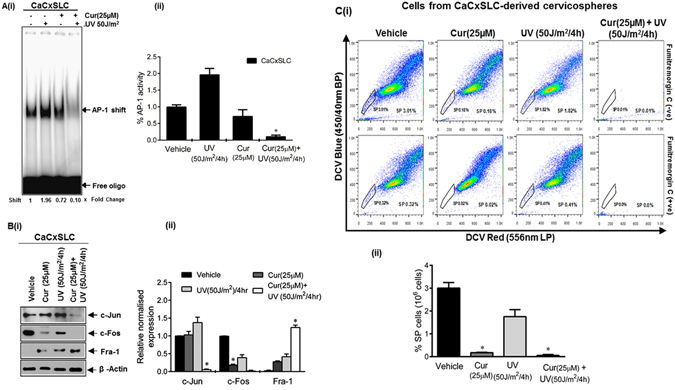
Effect of blocking AP-1 activity and expression by curcumin on SP cells. (A) Effect on AP-1 DNA-binding activity. Representative autoradiogram of nuclear protein (10 µg/lane) from day10 cervicospheres cultures treated with curcumin and/or UV co-incubated with labelled AP-1 probe and run on 5% native PAGE as described in Methods (i). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (ii). *p-value < 0.05 vs. vehicle treated cells from CaCxSLC-derived cervicospheres. (B) Immunoblot analysis of treated cells as described above. Representative cropped blots showing expression levels of AP-1 family members in day10 cervicospheres cells post-treatment of vehicle or cucurmin or UV or both. β-actin was used as input control (i). The gels were run under the same experimental conditions. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (ii). *p-value < 0.05 vs. vehicle treated cells from CaCxSLC-derived cervicospheres. (C) Curcumin eliminates SP cells post UV-irradiation. Dot-plot showing flowcytometric analysis of enzymatically dissociated and pooled cells from CaCxSLC-derived cervicospheres stained with DCV and/or FTC and incubated further with vehicle or curcumin alone for 24 h and subjected to UV radiation for 4 hr and cultures were left for another 12 hr for assessment of % SP cells in 106 cells (i). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (ii). *p-value < 0.05 vs. vehicle treated cervicospheres cells.
