FIGURE 4.
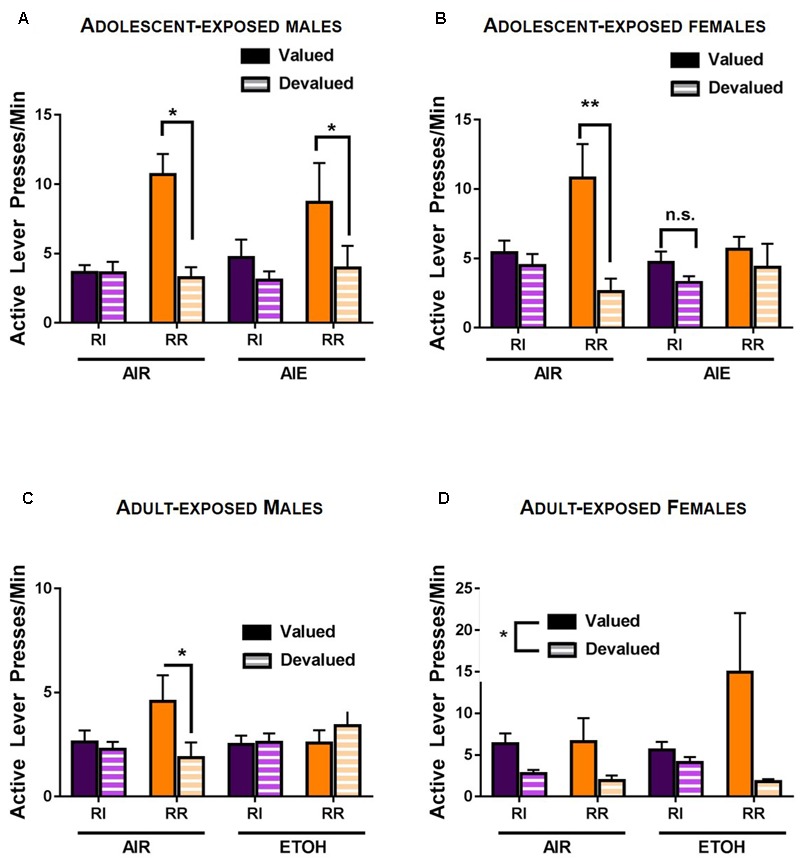
Response strategy selection in an outcome devaluation test in adult rats following ethanol exposure. (A) In adult male rats, responding on the RI habit-promoting lever was habitual in both air control and AIE exposed groups, as evidenced by a lack of reduction in response rate when the outcome was devalued by specific satiety. In contrast, responding on the RR lever was goal-directed (sensitive to outcome devaluation) in male rats in both the control (AIR) and ethanol exposed groups. (B) AIR exposed female rats showed similar patterns of responding to males. In control female rats, responding on the RI schedule was habitual (i.e., was insensitive to outcome devaluation), while responding on the RR lever was goal-directed and sensitive to outcome devaluation. In contrast, AIE exposed females showed habitual response strategies on both the RI lever and the RR lever; responding on both the RR and RI levers was insensitive to outcome devaluation. (C) Air exposed male rats were insensitive to outcome devaluation on the RI lever, consistent with habitual behavior, but were sensitive to outcome devaluation on the RR lever, indicative of goal-directed actions. In contrast, adult ETOH exposed males were insensitive to outcome devaluation on both levers, indicative of habitual response strategies during responding in both action- and habit-promoting conditions. (D) In female rats, a main effect of devaluation was present, indicating lower response rates during devaluation in all conditions. This was not mediated by schedule or adult ethanol exposure. ∗p < 0.05.
