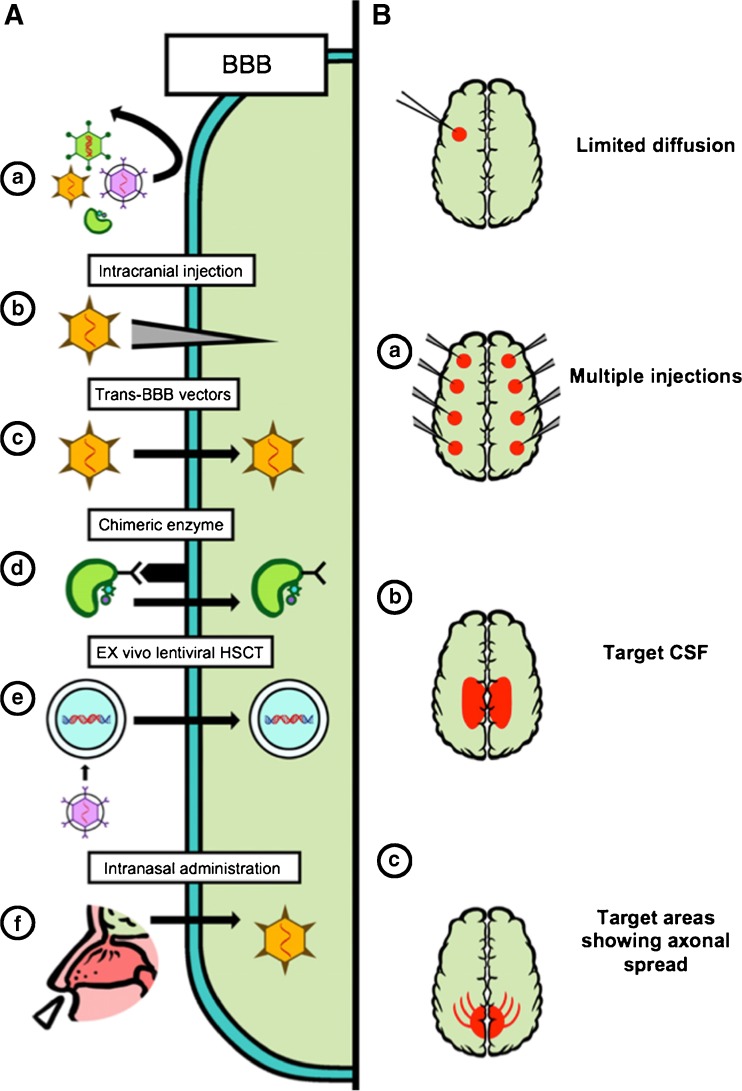
Fig. 5.
Direct in vivo gene transfer in CNS. A: a) The BBB prevents most viruses and enzymes from entry into the CNS. (b) Intracranial injections (c) Certain AAV can cross the BBB (d) The enzyme can be modified to have affinity for receptors that traffic proteins across the BBB (e) Haematopoietic stem cells can be transfected ex vivo, then reintroduced to the patient. They can cross the BBB, carrying the transfected gene into the CNS. (f) Intranasal virus delivery. B: (a) Multiple injections to target multiple areas (b) CSF target to distribute the virus (c) Target areas of axonal spread (Rastall and Amalfitano 2015)