Fig. 8.
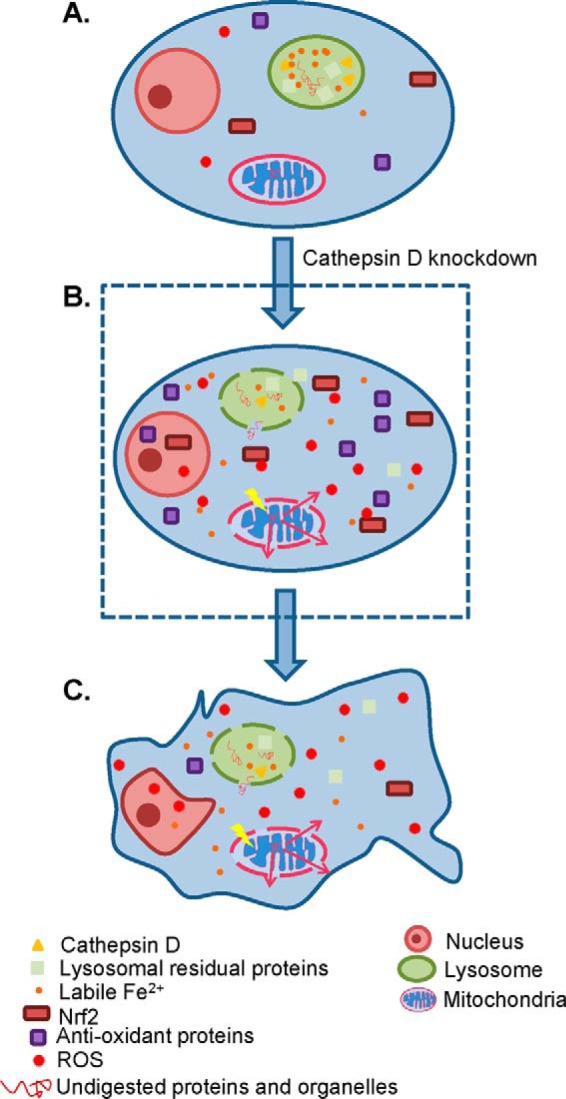
Schematic diagram of cathepsin D knockdown induced biological events. A, A normal HeLa cell is depicted, and the lysosomal contents, including cathepsin D, other lysosomal residual proteins, Fe2+, and undigested proteins and organelles, are well retained within lysosome. B, The knockdown of cathepsin D increases LMP and decreases ΔMMP, followed by ROS accumulation. The elevation of ROS transiently activates Nrf2 and promotes the transcription of many antioxidant proteins. C, Persistent oxidative stress because of lysosome rupture and mitochondria leakage, however, serves to inhibit the Nrf2 transcriptional activity and reduces the amount of antioxidant proteins, thus further aggravates oxidative stress within cells and finally leads to cellular senescence.
