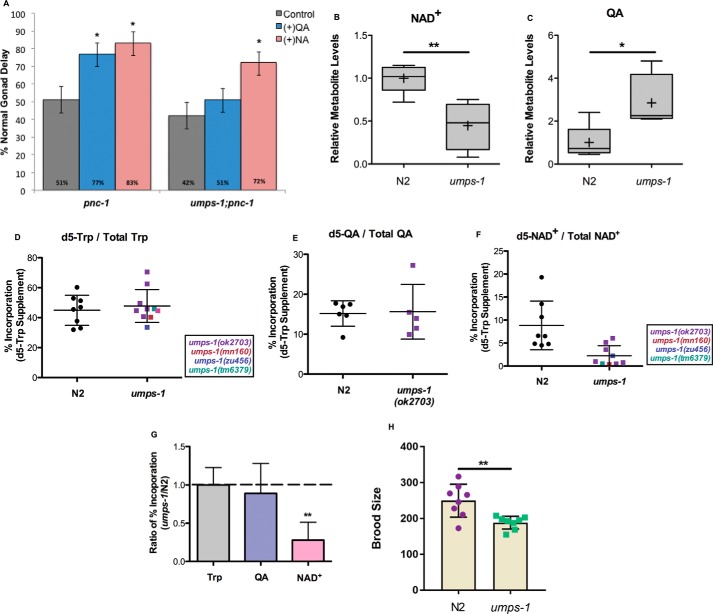
Figure 3.
UMPS-1 is required for NAD+de novo synthesis. A, supplementation of QA to pnc-1(pk9605) mutants restores the gonad developmental delay but has no effect on umps-1(ok2703);pnc-1(pk9605) animals, whereas supplementation of NA restores gonad development in both genetic backgrounds. Note that the penetrance of the gonad development phenotype is influenced by food type (15, 18). The penetrance is lower (more normal animals) in this experiment than that reported in Fig. 2B. These animals were supplemented on culture plates with UV-killed food, whereas the supplementation reported in Fig. 2B was performed in liquid culture with heat-killed food, which exacerbates the phenotype. Error bars are S.D. *, 0.01 < p < 0.05; **, 0.001 < p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; calculated with Fisher's exact test. B and C, LC-MS measurements of relative levels of NAD+ (B) and QA (C) in N2 and umps-1(ok2703) mutant animals. Plots are described in legend to Fig. 1B. *, 0.01< p < 0.05; **, 0.001 < p < 0.01; calculated with Welch's two sample t test. D–F, percent incorporation of isotope label from d5-Trp supplementation into the Trp pool (D), the QA pool (E), and NAD+ pool (F) in N2 and umps-1 mutant animals. Data derived from a variety of alleles of umps-1 are provided and differentiated via the color code on the figure panel. G, ratio of percent isotope label incorporated into Trp, QA, and NAD+ in umps-1(ok2703) mutants compared with N2. Error bars indicate S.D. Plots are as described in Fig. 1B. **, 0.001 < p < 0.01, calculated with Welch's two sample t test. H, progeny production is reported for N2 control and umps-1(ok2703) mutant animals. **, 0.001 < p < 0.01; calculated with Student's t test.