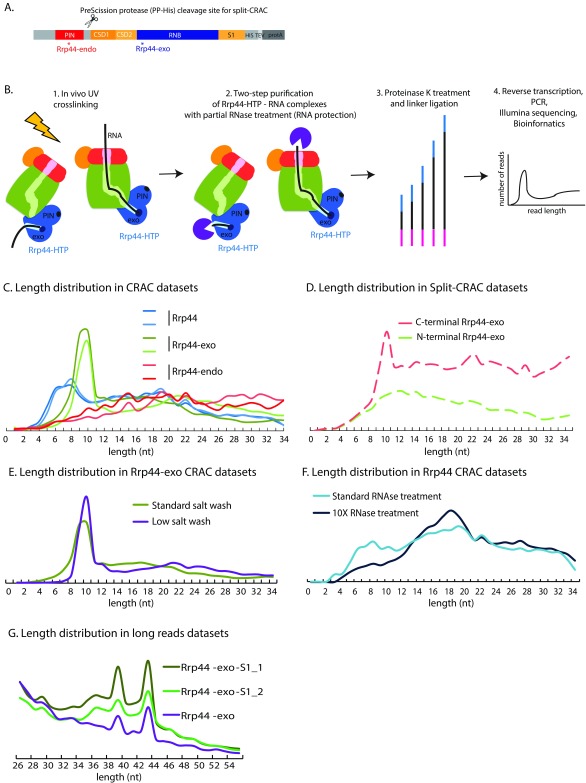
Figure 1. Exosome structure and interactions.
( A) Domain structure of the Rrp44-HTP fusion. From N-terminus to C-terminus, the following domains are indicated: PIN domain harboring endonuclease activity, CSD (Cold-Shock RNA binding domain), RNB (ribonuclease) domain harboring exonuclease activity, S1 RNA binding domain and the HTP-tag (His 6, TEV protease cleavage site, protein A). Asterisks represent location of point mutations in Rrp44-endo and Rrp44-exo. The PreScission protease cleavage site and associated His6 tag (PP-His) used in split-CRAC is represented as scissors. ( B) Overview of the CRAC experiment on Rrp44-HTP. The main components of the exosome are schematically represented: the cap in red, the RNase PH-ring in green. The PIN endonuclease and exonuclease (exo) active sites of Rrp44 are indicated in dark blue. Exponentially growing cells were UV crosslinked (1), RNA associated with Rrp44, either by threading or direct access, was purified via a two-step purification involving partial RNase treatment (2), processed by linker ligation followed by proteinase K digestion (3), reverse-transcribed, PCR amplified and Illumina sequenced (4). ( C) Length distribution of reads recovered in CRAC datasets for Rrp44, Rrp44-exo or Rrp44-endo. Two independent experiments for each protein are shown. ( D) Length distributions of reads recovered with Rrp44-exo N-terminal and C-terminal regions, obtained by split-CRAC. ( E) Length distribution of reads recovered by Rrp44-exo CRAC using either standard salt washes (used for all other CRAC datasets presented in this study, 1M NaCl, green line) or standard salt washes (350nM NaCl, purple line). ( F) Length distribution of reads recovered by Rrp44 CRAC using either standard RNase treatment (used for all other CRAC datasets presented in this study, light blue line) or 10X RNase treatment (dark blue line). ( G) Length distribution of long reads recovered by Rrp44-exo (purified with 350 nM NaCl, sequenced on 150nt Illumina run) and Rrp44-exo-S1 CRAC (purified with 1M NaCl, sequenced on 100nt Illumina run).