Fig. 3.
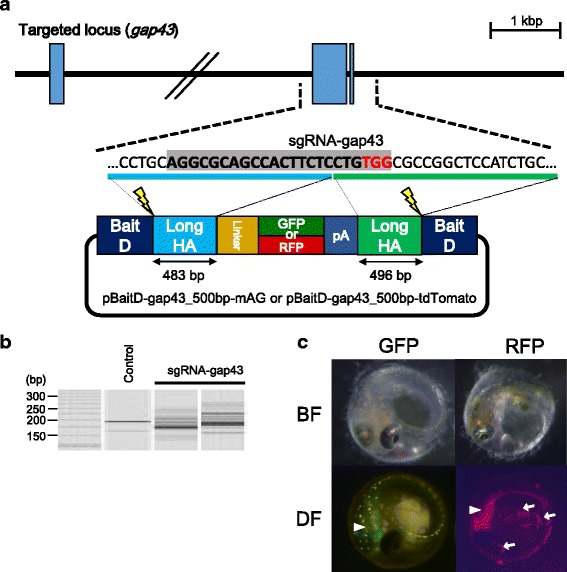
Targeted gene integration of GFP or RFP constructs containing BaitD into the gap43 locus. (a) Design of sgRNA and homology arms to target the second exon of gap43 gene (Ensembl transcript number ENSORLT00000015837). The donor plasmids contain two BaitD sequences, upstream and downstream homology arms, and monomeric Azami-Green (mAG; as GFP) or tandem-dimer-Tomato (tdTomato; as RFP) with a N-terminal linker and a SV40 polyA signal (pA). The upstream or downstream homology arms (483 or 496 bp) for the donor plasmids are shown in boxes with light blue or green color, respectively. (b) The genome-editing activity by the sgRNA targeting to the gap43 locus (sgRNA-gap43), which was investigated using the heteroduplex mobility assay (HMA) of embryos injected with a mixture containing 100 ng/μL of Cas9 mRNA and 50 ng/μL of sgRNA-gap43. Control shows the result from an embryo without injection. (c) GFP and RFP expression in the injected embryos at 4 days post fertilization (dpf). Embryos injected with the donor vectors expressed either GFP or RFP in their central nervous system (CNS). White arrowheads show fluorescence in the CNS, while white arrows show autofluorescence of bacteria on the surface of the egg membrane
