Fig. 4.
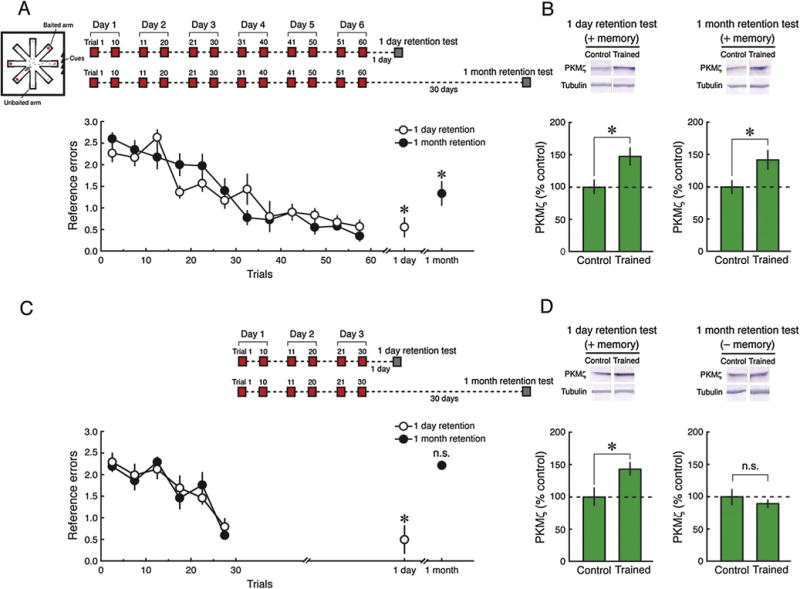
Increased PKMζ persists in dorsal hippocampus 1 month after radial arm maze conditioning. (A) Inset above left, schematic representation of radial arm maze with 4 of 8 arms baited. The baited and empty arms remain the same throughout the training and retention testing. Inset above right, schematic diagram of 6-day training protocol producing 1-month memory. Training consists of 10 trials per day for 6 days, and retention testing is either 1 day or 1 month later. Below, decrease of reference memory errors over 6 days of training and for both 1 day and 1 month after training; mean ± SEM. There is a main effect of training phase (beginning of training, end of training, retention) (F2,24 = 62.83, P < 0.0001), and interaction between group (1 day retention, 1 month retention) and training phase (F2,24 = 3.68, P < 0.05). Tukey post hoc tests reveal that the reference errors in the retention test are significantly lower than at the beginning of training (1 day retention, n = 6, P < 0.001; 1 month retention, n = 8, P < 0.001). (B) Above, representative immunoblots; below, mean ± SEM, showing increases in dorsal hippocampal PKMζ both 1 day and 1 month after 6 days of training (1 day post-training: n’s = 6, t10 = 2.76, P < 0.05; 1 month post-training: control, n = 6, trained, n = 8, t12 = 2.23, P < 0.05). (C and D) Memory and increased dorsal hippocampal PKMζ induced by 3 days of radial arm training persist for 1 day but not for 1 month. (C) Inset above, schematic diagram of 3-day training protocol producing memory retention for 1 day but not 1 month. Training consists of 10 trials per day for 3 days, and retention testing is either 1 day or 1 month later. Below, decreases of reference memory errors during training and for 1 day but not 1 month memory after training; mean ± SEM. There is a main effect of group (1 day retention, 1 month retention) (F1,10 = 10.74, P < 0.01), training phase (beginning of training, end of training, retention) (F2,20 = 34.08, P < 0.0001), and interaction between group and training phase (F2,20 = 16.49, P < 0.0001). Tukey post hoc tests reveal that reference errors are significantly lower than at the beginning of training in the 1-day retention test (n = 6, P < 0.001), but not in the 1-month retention test (n = 6, P = 0.99). (D) Above, representative immunoblots; below, mean ± SEM, showing increases in dorsal hippocampal PKMζ at 1 day after 3-day training, but no significant change at 1 month (1 day post-training: control, n = 6, trained, n = 5, t9 = 2.42, P < 0.05; 1 month post-training: control, n = 5, trained, n = 6, t9 = 0.82, P = 0.44).
