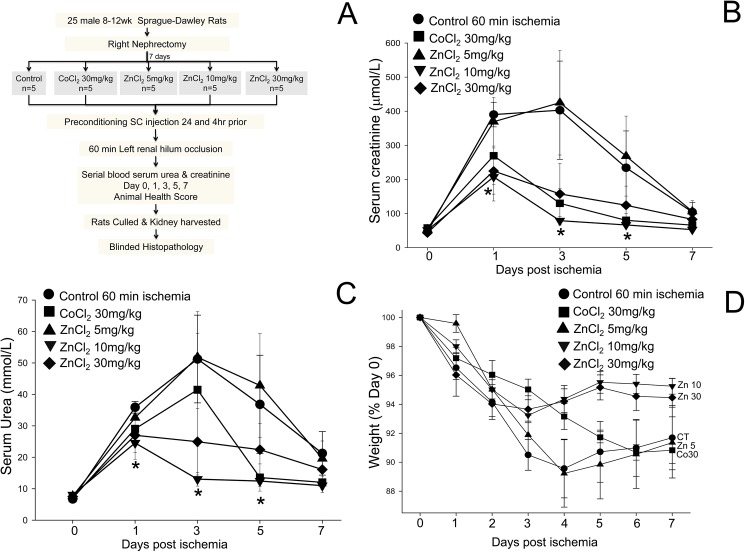
Fig 2. Zinc preconditioning protects against renal ischemia reperfusion injury in rats.
(A) Diagram showing the experimental protocol. (B) Serum creatinine concentrations (mean ± SEM (μmol/L)) in rats treated with saline (control) (●), 30 mg/kg cobalt (■), 5 mg/kg ZnCl2 (▲), 10 mg/kg ZnCl2 (▼) or 30 mg/kg ZnCl2 (◆). The rise in serum creatinine was less in rats preconditioned with 10mg/kg ZnCl2 than in the saline control group. (C) Serum urea concentrations (mean ± SEM (mmol/L)). The rise in serum urea was less in rats preconditioned with 10 mg/kg ZnCl2 than in the saline control group. (D) ZnCl2 preconditioning improves the health of rats after IRI. The slope (-0.51) of the line of regression for weight loss in the rats treated with 10 mg/kg ZnCl2 was less than the slope for rats treated with 30 mg/kg cobalt (-1.32) or saline (-1.15). *p<0.05 Vs saline treated control. On repeated measures ANOVA, including days one to seven, there was a statistically significant difference between- 10 mg/kg ZnCl2 Vs Saline control (p = 0.038).